Lecture
A dentist is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases of the teeth, gums, jaws, and the entire oral cavity. He can perform a wide range of procedures: from filling and extracting teeth to complex surgeries and installing implants. Dentistry includes many narrow specializations: therapeutic, orthopedic, surgical, orthodontics, periodontology, etc.
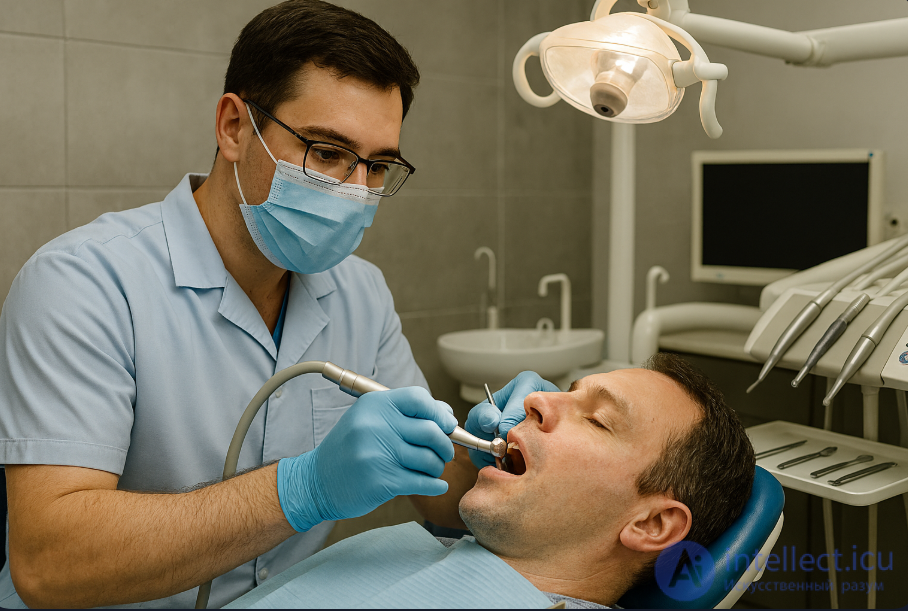
Diagnosis of diseases
Conducting an examination of the oral cavity, teeth, gums and jaws.
Use of instrumental and radiological diagnostic methods.
Making a preliminary and final diagnosis.
Treatment of patients
Treatment of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis and other dental diseases.
Carrying out therapeutic, surgical, orthopedic or orthodontic procedures (depending on specialization).
Tooth extraction, installation of fillings, dentures, implants.
Carrying out preventive measures (professional teeth cleaning, fluoridation, sealing).
Treatment appointments and consultations
Development of an individual treatment plan.
Prescription of drug therapy (painkillers, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs).
Providing patients with advice on oral hygiene and disease prevention.
Preventive work
Conducting health education work with patients.
Formation of correct hygiene skills in children and adults.
Working with medical documentation
Maintaining outpatient patient records, entering data on diagnoses and treatment performed.
Preparation of reporting documentation.
Ensuring safety and sanitation
Compliance with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis.
Ensuring sterility of instruments and workplace.
Compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
Advanced training
Study of new methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Improving the level of professional knowledge and skills.
To become a dentist, you must have:
Excellent vision and coordination of movements
With a steady hand and high motor precision
Knowledge of anatomy, physiology, pharmacology and microbiology
Ability to work with X-rays, instruments and equipment
Skills of sterile work and compliance with sanitary standards
The work of a dentist requires not only medical training, but also a stable psyche:
Empathy and ability to communicate with patients, including children and people with phobias
Stress resistance - especially in difficult or emergency situations
Patience and attention to detail
The ability to maintain concentration for long periods of time
Ability to work in a team and make decisions
To obtain the right to practice, you must:
Graduate from a medical university with a degree in Dentistry (usually 5 years)
Complete an internship or residency (1–2 years depending on specialization)
Get a Dentist Certificate
Take refresher courses regularly (once every 5 years)
Specializations require additional training: for example, orthodontics, surgery, pediatric dentistry, etc.
| Country | Average salary/year |
|---|---|
| USA | $160,000–$220,000 |
| Canada | $120,000–$180,000 |
| Germany | $90,000–$130,000 |
| United Kingdom | $80,000–$110,000 |
| UAE | $100,000–$150,000 |
| Ukraine | $12,000–$18,000 |
| China | $13,000–$72,000 |
| India | $8,000–$15,000 |
Earnings vary greatly depending on experience, specialization, place of work (public or private clinic), as well as country and region.
Dentists are exposed to a number of risks:
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system (osteochondrosis, varicose veins, back and neck pain)
Visual impairment
Allergies to dental materials
Psycho-emotional burnout
Infectious diseases (if sanitary standards are violated)
Dentistry covers many specializations and related professions:
Dentist-therapist
Dentist-surgeon
Orthodontist
Periodontist
Implantologist
Children's dentist
Orthopedic dentist
Dental Hygienist
Dental technician
Dental assistant
Medical representative of a pharmaceutical company
Each of these professions requires separate training and certification, but they all work in the field of oral health.
Comments
To leave a comment
Professions and specialties
Terms: Professions and specialties