Lecture
The random variable magnitude is the numerical characteristic of the distribution of a given random variable.
If given a random variable 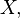 defined on a certain probability space, then:
defined on a certain probability space, then:
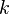 initial moment of random variable
initial moment of random variable 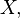 Where
Where 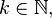 called magnitude
called magnitude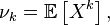
if the expectation is 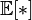 on the right side of this equation is defined;
on the right side of this equation is defined;
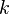 th center moment of a random variable
th center moment of a random variable 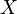 called magnitude
called magnitude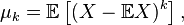
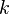 absolutist and
absolutist and 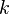 m absolute absolute moments of a random variable
m absolute absolute moments of a random variable 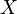 is called according to size
is called according to size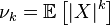 and
and 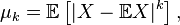
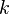 m factorial moment of a random variable
m factorial moment of a random variable 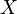 called magnitude
called magnitude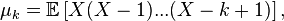
if the expectation on the right side of this equation is defined. [one]
Absolute moments can be defined not only for integers 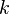 but for any positive real if the corresponding integrals converge.
but for any positive real if the corresponding integrals converge.
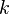 th order, then determined and all the moments of lower orders
th order, then determined and all the moments of lower orders 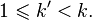
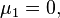
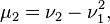
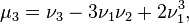
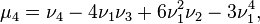 etc.
etc.
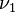 equals the mathematical expectation of a random variable and shows the relative location of the distribution on the number line.
equals the mathematical expectation of a random variable and shows the relative location of the distribution on the number line.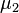 equals the distribution variance
equals the distribution variance 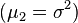 and shows the spread of the distribution around the mean.
and shows the spread of the distribution around the mean.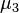 being properly normalized, is a numerical characteristic of the symmetry of the distribution. More precisely, the expression
being properly normalized, is a numerical characteristic of the symmetry of the distribution. More precisely, the expression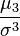
called the asymmetry coefficient.
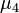 controls how pronounced the vertex of the distribution is in the neighborhood of the middle. Magnitude
controls how pronounced the vertex of the distribution is in the neighborhood of the middle. Magnitude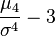
called the coefficient kurtosis kurtosis distribution 
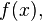 we have:
we have: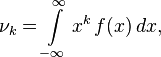
if a 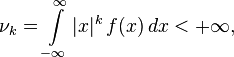
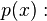
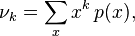
if a 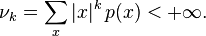
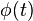 :
: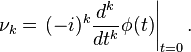
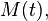 then the moments can be calculated by the following formula:
then the moments can be calculated by the following formula: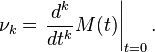
You can also consider non-integer values. 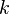 . Moment considered as a function of the argument
. Moment considered as a function of the argument 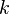 is called the Mellin transform.
is called the Mellin transform.
You can consider the moments of a multidimensional random variable. Then the first moment will be a vector of the same dimension, the second will be a second-rank tensor (see covariance matrix) over a space of the same dimension (although a trace of this matrix can be considered, which gives a scalar generalization of the variance). Etc.
Comments
To leave a comment
Probability theory. Mathematical Statistics and Stochastic Analysis
Terms: Probability theory. Mathematical Statistics and Stochastic Analysis