Lecture
Suppose event B can only occur with one of the incompatible events. 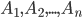 . For example, the store receives the same products from three enterprises in different quantities. There is a different likelihood of low-quality products in different enterprises. Randomly selected one of the products. It is required to determine the probability that this product is of poor quality (event B). Here are the events
. For example, the store receives the same products from three enterprises in different quantities. There is a different likelihood of low-quality products in different enterprises. Randomly selected one of the products. It is required to determine the probability that this product is of poor quality (event B). Here are the events 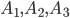 - is the choice of products from the products of the relevant company.
- is the choice of products from the products of the relevant company.
In this case, the probability of an event B can be considered as the sum of the products of events.
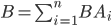
By the addition theorem of probabilities of incompatible events we get
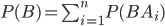
Using the probability multiplication theorem, we find
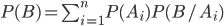 (3.1)
(3.1)
Formula (3.1) is called the formula of total probability .
Example. For the case considered above with the arrival of goods in the store from three companies, we will assign numerical values. Suppose that the first enterprise received 20 products, from the second - 10 products and from the third - 70 products. The probabilities of poor-quality product manufacturing at enterprises are respectively 0.02; 0.03 and 0.05.
Determine the probability of taking a poor quality product.
Decision. Probabilities of events 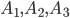 will be equal to P (A1) = 0.2; P (A2) = 0.1; P (A3) = 0.7. Using formula (3.1), we find
will be equal to P (A1) = 0.2; P (A2) = 0.1; P (A3) = 0.7. Using formula (3.1), we find
P (B) = 0.2 × 0.02 + 0.1 × 0.03 + 0.7 × 0.05 = 0.042.
Comments
To leave a comment
Probability theory. Mathematical Statistics and Stochastic Analysis
Terms: Probability theory. Mathematical Statistics and Stochastic Analysis