Lecture
Let event B occur simultaneously with one of the n incompatible events A1, A2, A3, ... An . It is required to find the probability of event Ai , if it is known that event B has occurred.
Based on the probability theorem of the product of two events, one can write
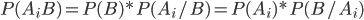
From where
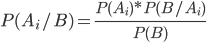
or
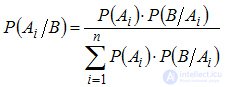 (3.2)
(3.2)
Formula (3.2) is called the Bayes formula .
Example. Three organizations submitted accounts to the control department for random inspection. The first organization submitted 15 invoices, the second - 10, the third - 25. The probabilities of the correct issuance of invoices for these organizations are known and, accordingly, are: 0.9; 0.8; 0.85. One account was selected and it turned out to be correct. Determine the probability that this account belongs to the second organization.
Decision. Let be 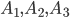 - Account selection events at the first, second and third organizations. The corresponding probabilities will be
- Account selection events at the first, second and third organizations. The corresponding probabilities will be
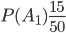 ,
, 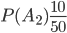 ,
, 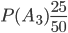
According to the formula of total probability, we determine the probability of choosing a properly executed account.
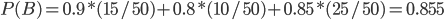
By the Bayesian formula we find the initial probability.
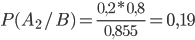 .
.
Comments
To leave a comment
Probability theory. Mathematical Statistics and Stochastic Analysis
Terms: Probability theory. Mathematical Statistics and Stochastic Analysis