Lecture
The shadow of any flat geometric object can be constructed as a set of shadows of the points and lines that make up this object.
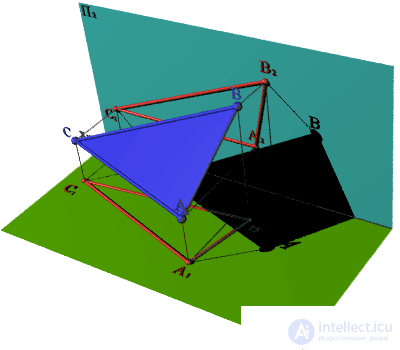
A planar geometric object can be turned to the observer by the lit or unlit side (that is, the side in its own shadow).
|
|
|
|
|
There is a practical method for determining your own shadow: if, when traversing the vertices of the projections of any polygon and the vertices of its falling shadow in the same direction, the order of designation is the same, then the visible side of the plane is lit.
Comments
To leave a comment
Descriptive Geometry and Engineering Graphics
Terms: Descriptive Geometry and Engineering Graphics