Lecture
The direction of light rays in perspective is determined by two geometrical parameters:
1. α - the angle of inclination of the light rays to the subject plane P 1 .
2. b - the angle of inclination of the horizontal projections of the light rays to the picture plane K.
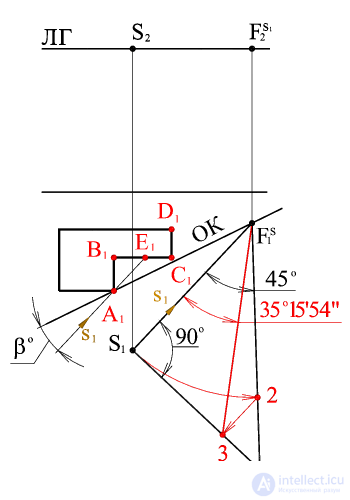
The angle of inclination of the light rays to the object plane is taken to be equal to the angle of inclination of the diagonal of the cube, whose faces coincide with the planes of the projections, α = 35 o 15'54 " .
The angle of inclination of the horizontal projections of the light rays to the picture plane is selected depending on the configuration of the imaged object and on the required light intensity.
|
|
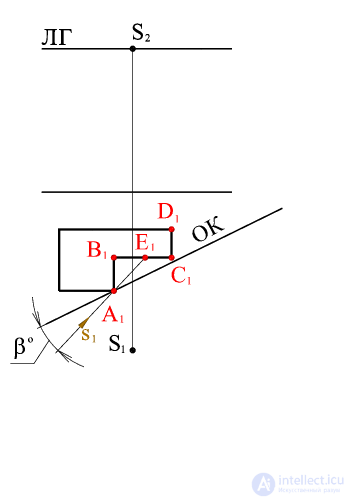
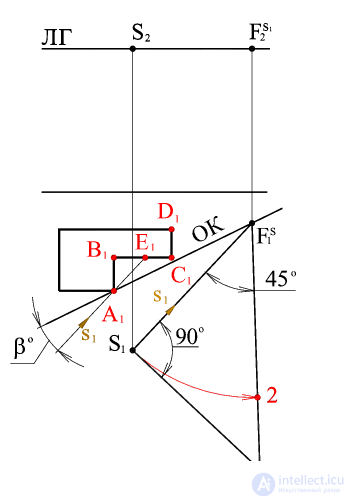
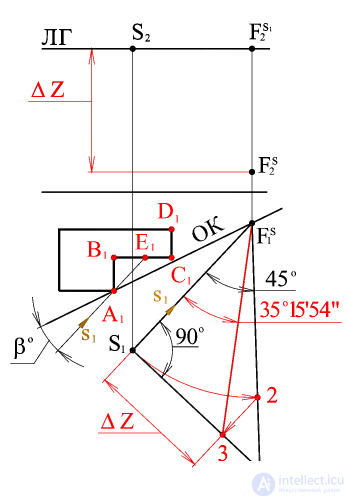
Consider an algorithm for choosing the direction of light rays, determining the vanishing points of light rays and their horizontal projections. Set the direction of the horizontal projections of the light rays s 1 , i.e. choose angle b depending on the desired illumination of a given object. Let the light source (the sun) is located to the left of the observer so that the walls of the building AB and CD will be in their own shadow. Depending on the angle b, the illumination of the wall of the building sun changes (part of the wall of the BE will be in the falling shadow from the wall AB ). Thus, the angle value is chosen so that the desired part of the wall of the building sun is in the shade. |
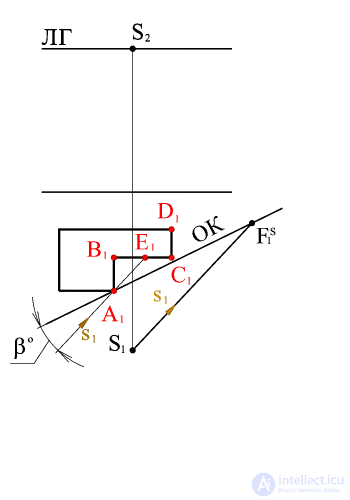
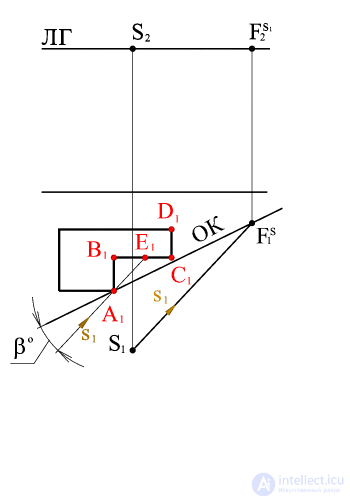
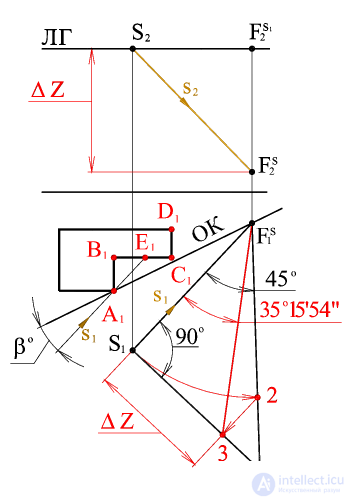
Through the horizontal projection of the point of view of S 1 we draw a beam parallel to the horizontal projection of the light beam s 1 , before the intersection with the base of the picture at the point F S 1 (the horizontal projection of the vanishing point of the horizontal projections of the light rays). From this point, draw a projection line to the intersection with the horizon line. The resulting point is the vanishing point of the horizontal projections of the light rays.
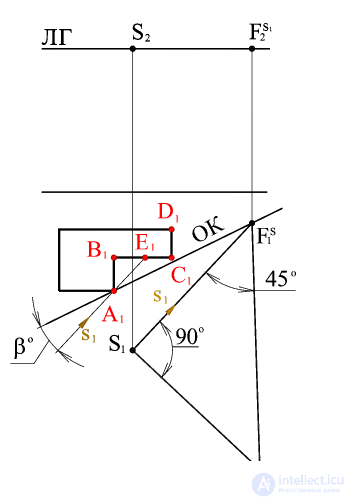
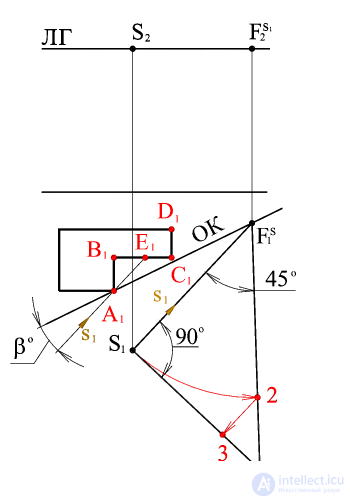
From points F S 1 and S 1 are held straight at an angle of respectively 45 and 90 o to the horizontal projection of the light beam, which intersect at point 1 .
We build an angle of 35 ° 15'54 "- the natural size of the angle of inclination of the light rays to the object plane.
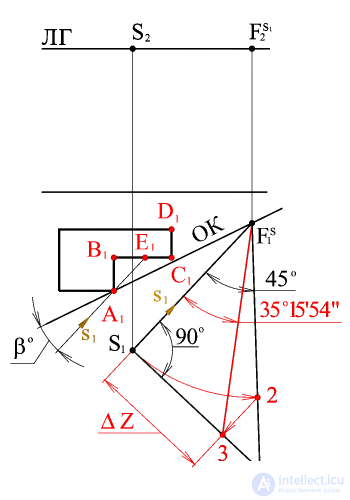
The segment S 1 3 determines the difference of the coordinates D Z of vanishing points F S light rays and f s 1 horizontal projections of light rays.
Comments
To leave a comment
Descriptive Geometry and Engineering Graphics
Terms: Descriptive Geometry and Engineering Graphics