How to build internal and external mates of a given radius for circles?
When constructing the conjugation of two circles by the arc of the third circle of a given radius, three options are possible: external conjugation, internal conjugation, and a combination of external and internal conjugations.
Before building mates in AutoCAD, let's remember what mating is and how mates are built for two circles.
Conjugation is the smooth transition of one line (straight or curved) to another. The point at which one line passes to another is called a pairing point . When drawing mates, it is necessary to construct the center of the conjugating arc and determine the points of conjugation or tangency.
Let us analyze in order each variant of the conjugation of two circles.
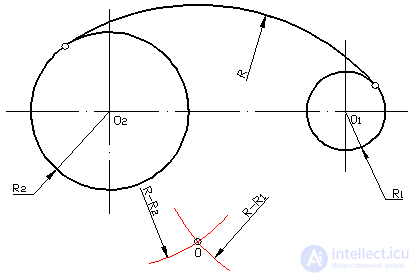
External conjugation of circles by an arc of a given radius R.
The mating arc touches specified circles on the outside. The center O of the conjugating arc must be separated from the circles at the same distance, equal to R. To construct the center O of the conjugating conjugating arc, from the centers of the circles O 1 and O 2, we draw two auxiliary arcs with radii ( R + R 1 ) and ( R + R 2 ) until they intersect each other. The points of conjugation lie on the lines connecting the centers of the circles.
Answers to users' questions on AutoCAD
Copyright 2007-2012 Ivan Boyarsky.
Well, I hope everything is clear with theory. We proceed to the implementation of the foregoing with respect to AutoCAD. Of course, you can go to the specified path, build auxiliary circles to find the center of the arc of a pairing, build a mate and remove auxiliary circles. You can go more simple way. AutoCAD has the FILLET tool, but it can only build an external mate :(
How to deal with the other two cases of pairings?
There is an exit! And it is quite simple! As they say, all ingenious is simple!
To build all the specified mates, it is enough to construct a circle at two points of tangency with a given radius of the mate arc! In the above drawings, the touch points are indicated by small circles. Well, then only remains to trim the excess ...
How to build a circle at two points of contact with a given radius?
To do this, go to the menu Drawing - Circle :
Internally, the conjugation of circles by an arc of a given radius R.
The mating arc touches specified circles by the inner side. The center O of the conjugating arc is determined by the intersection of the arcs of the auxiliary circles, the radii of which are equal to the differences ( RR 1 ) and ( RR 2 ).
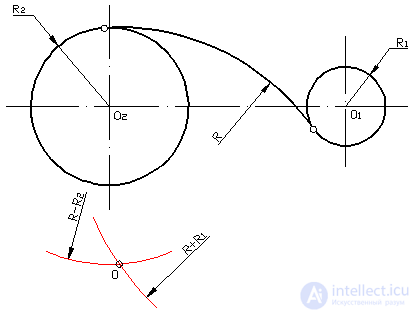
The combination of external and internal conjugations of circles by an arc of a given radius R.
One of the given circles is inside the mating circle. The center O of the conjugating arc is determined at the intersection point of the auxiliary circles drawn for the external conjugation with a radius ( R + R 1 ), and for the inner circumference - with a radius ( RR 2 ).
I hope you have succeeded.

Comments
To leave a comment
Descriptive Geometry and Engineering Graphics
Terms: Descriptive Geometry and Engineering Graphics