The ratio of the opposite leg to the hypotenuse is called the
sine of the acute angle of a right triangle.
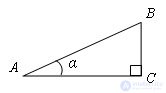
The sine of the angle α is denoted by: sin α.
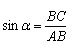 The tangent of the angle of a
The tangent of the angle of a right-angled triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg to the adjacent leg. The tangent of the angle α is indicated: tg α.
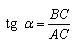 Theorem.
Theorem. The sinus and tanngs of the angle, like the cosine, depend only on the angle.
Evidence. Let ABC be a given right triangle, then by the Pythagorean theorem
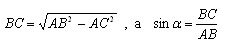
a
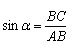
Then
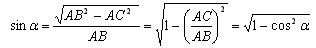
And since cos depends only on the magnitude, sin also depends only on the magnitude.
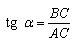
Divide the numerator and denominator by AB:
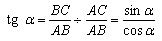
And since cos and sin depend only on the angle, tg also depends only on the angle. The theorem is proved.

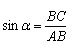
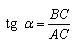
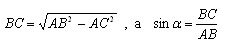
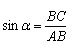
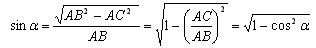
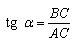
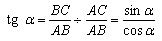
Comments
To leave a comment
Planometry
Terms: Planometry