1. Do I need to use keywords in the URL?
The presence of keywords in the URL is an additional hint for the PS about the page content and one of the ranking factors.
Screenshot of https://yandex.ru/support/webmaster/recommendations/site-structure.xml

In addition, keywords in the URL improve the clickability of the site - if they match the request, the URLs are highlighted and help the user to better navigate your site.
We recommend using keywords in the URL, but not “spamming”.
Let's take a look at what will be considered spam in a URL:
Example number 1: "Repetition of keywords"
intellect.bond/catalog/detskaya-obuv/detskaya-obuv-dlya-malchikov/demisezonnaya-detskaya-obuv-dlya-malchikov/
Search engines may consider spamming such a repetition of the keyword detskaya-obuv .
Correctly:
intellect.bond/catalog/detskaya-obuv/dlya-malchikov/demisezonnaya/
Example number 2: "Spam phrase design"
intellect.bond/catalog/nozhi-skladnye-kupit-moskva/
“Nozhi-skladnye-kupit-moskva” is an unnatural spam construction. It is necessary to use phrases according to the rules of the Russian language.
Correctly:
intellect.bond/catalog/skladnye-nozhi/
Example # 3: “URL coincides with title, h1”
Screenshot:
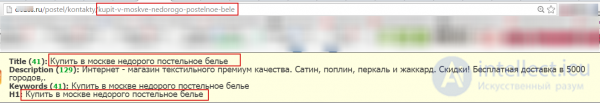
We recommend avoiding such a construction, since if there are other signs of spam on the site, it may serve as a signal for imposing sanctions.
In this case, the correct way is:
intellect.bond/postel/kontakty/postelnoe-bele/
2. Site 5 years. I would like to translate the site to CNC. What reaction to expect from search engines? Do I need to go to the CNC at all or leave it as it is?
The advantages of using CNC are known for a long time, in particular:
- you can use keywords;
- CTR (click-through rate) increases as keywords are highlighted in the output;
- about the essence of the page to which the user is going to go;
- easier to remember.
But what if the site has long been launched and receives traffic from the PS? Is it worth it to go to the CNC?
If the subject of the site is competitive, and the site occupies the top positions on the requests of interest, you should not translate the site to CNC - in this case, the translation may not always be justified.
If the site for most requests is ranked for the TOP-10, then it is better to transfer it to CNC. Properly configured CNC positively evaluated by search engines, which will give a plus in the ranking of the pages of your site.
Yandex recommendations, paragraph 4.
Google recommendations:
Screenshot https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/76329?hl=en
Of course, there can be no completely painless transition - for some requests for a position, respectively, traffic can jump, it will take some time to recover.
If the CNC is set up correctly, and immediately after the appearance of the new version of the URL, page-by-page 301 redirects are made, then subsidence will be minimal or it will not exist at all. Within a month after the change, traffic / positions will be restored and improved.
Recommendations that should be followed when drawing up the CNC:
- when creating a URL, choose those words that are directly associated with the goal of the page and give a brief idea of its content;
- CNC should be organized in such a way that the address reflects the structure of the site;
- always use a hyphen to separate words in the URL;
- URL length must be limited to 60-80 characters.
3. Urls containing parameters appeared in the search engine index, which resulted in duplicates, for example:

What advise in this situation?
URL parameters allow you to track various statistics and evaluate the effectiveness of advertising campaigns. On the one hand, the use of parameters in the URL is useful for tracking the source of traffic, on the other hand, this leads to the appearance of duplicates.
To prevent the URL parameters from interfering with normal indexing and ranking of the site, we recommend that the attribute rel = "canonical" be added to the site. This way you will tell the robots which particular page from the duplicate group is the main (canonical) one.
- Yandex recommendations on using rel = canonical
- Google recommendations for rel = canonical
4. Which links are better to do: translit, translation or Cyrillic? For example: intellect.bond/link, intellect.bond / link, intellect.bond / ssylka.
According to the study of Igor Bakalov, Cyrillic URLs are preferable for Yandex, then the translation, and in the last place, transliteration.
For Google, the translation is preferable, Cyrillic in second place, transliteration in third.
We can draw conclusions: if the promotion is preferable for Yandex - it is better to use the Cyrillic alphabet.
If under Google - better translation.
But! There are some flaws in using Cyrillic and translating into a URL in terms of usability.
The disadvantage of using Cyrillic URLs is that they become cumbersome and incomprehensible when copying.
For example, a URL like https:/интеллект.com//directory/Mobile-Phone/ will look like this:
https://xn--e1aahkdal4bf.com/%D0%BA%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B3/%D0%BC%D0%
BE% D0% B1% D0% B8% D0% BB% D1% 8C% D0% BD% D1% 8B% D0% B5-% D1% 82% D0% B5% D0% BB% D0% B5% D1% 84 % D0% BE% D0% BD% D1% 8B /.
The lack of use of translation - not all English words will be known and understood by a user with a poor knowledge of English, especially, a person who does not speak English at all.
Since the URL in transliteration prevails in Yandex and Google, and for Russian-speaking users, transliteration will carry meaning. We prefer to use transliteration.
We do not recommend using mixed URLs (translit + translation, Cyrillic + translit or Cyrillic + translation):
- this can be considered a sign of lack of professionalism;
- the user has to change the keyboard layout when typing the address.
5. The engine forms a CNC with capital letters, is that bad?
Search engines handle capital letters in URLs well, but we do not recommend them. For search engines, the addresses “intellect.bond/Category” and “intellect.bond/category” are different. If you dictate to a person or enter the URL “intellect.bond/Category” in your ad, how do you think how he will type it? Most likely, most will enter the URL in one register - the bottom. This problem is solved - you need to configure a 301 redirect, so that when dialing from the lower register, the user translates to an address with a capital letter. But is it necessary?
In an interview (back in 2012), Matt Cutts advised not to use capital letters in the URL, citing the fact that:
a) it is a sign of lack of professionalism;
b) for users there is no meaning which letter is used in the URL - uppercase or lowercase, which leads to a variety of errors (one of which we described above).
Therefore, we recommend using the URL in one register - the bottom.
6. What to use in the URL: hyphen or underscore?
Search engines understand both the underscore and the hyphen.
But to separate words, we recommend using a hyphen, as according to Matt Cut's statement, Google understands underscores as a sign of the union.
Google recommendations:
Screenshot https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/76329?hl=en

But! If your site has a page with a URL that uses underscores to separate words, do not rush to change it, since the presence of these signs has a very small effect on the ranking.
If you still decide to replace - do not forget to configure the 301 redirect, because if you replace the underscore with a hyphen in the URL, the page for the PS will be new, and it is probably already indexed, has weight, contains key queries.
7. What is the best way to finish the URL of the page: the right slash "/" or the extension ".html"?
Many webmasters on this topic differ opinions, some prefer the use of the extension ".html", as there is a logical end of the URL. Others use the slash "/", because in this case the URL is shorter, clearer and easier to remember.
Search engines equally index pages with the right slash "/", and with the extension ".html".
We prefer to use the URL without the extension ".html", because we believe that the shorter the URL, the better (without fanaticism, of course). However, I repeat: in terms of indexing and ranking there is no difference, rather, it’s a matter of taste.
8. Can the number of slashes in the URL influence the ranking? For example, pages with which URLs will be better ranked: intellect.bond/shop/moda/zhenskaja-odezhda/platya/platya-midi/ or intellect.bond/catalog/platya/platya-midi/?
The number of slashes in the URL does not affect the ranking. The ranking is affected by the number of clicks required to go to the desired page from the Main page.
For example, in the URL there can be 6 slashes - intellect.bond/shop/moda/zhenskaja-odezhda/platya/platya-midi/ , but you can go to the page from the Main in one click.
If we look from the point of view of convenience and perception, then we give preference to the second option - intellect.bond/catalog/platya/platya-midi .
9. Put the CNC, generated the URL in the online store. As a result, the URL length is 190 characters on some products, i.e. the address of the browser is not fully visible.
The question is: is it within acceptable limits or should it be reduced? Excessively long URL may be worse indexed PS?
According to Yandex recommendations, an excessively long URL may worsen the indexing of documents.
Screenshot of https://yandex.ru/support/webmaster/recommendations/indexing.xml 
But what exactly is the number of characters within the allowable?
In Yandex.Market recommendations, the maximum allowed number of characters in a URL is 512.
Screenshot of the page - https://yandex.ru/support/partnermarket/offers.xml: 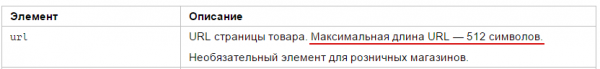
According to these recommendations, it can be assumed that Yandex normally indexes URLs up to 512 characters in length.
But, based on our own observations and experience, we advise when creating new URLs to focus primarily on the principles of usability and try to make the URL as informative as possible and, at the same time, as short as possible.
Here is an example of overly long URLs:

From the above examples, we see that URLs are inconvenient and not completely clear.
This URL length:
- poorly remembered;
- difficult to dictate;
- reduce the likelihood of input from the keyboard;
- go beyond the boundaries of the address bar in the browser;
- can be cut when copying;
- can be cut off by some social networks;
Page URL must be:
- concise;
- informative;
- logical;
- simple;
- display the essence of the page;
- display the structure of the site.
For example:

But, given that Yandex allows URLs up to 512 characters, we do not recommend reducing the already indexed CNC of such length.
Note! These recommendations should be analyzed and implemented at the stage of site creation.
If the URLs of the pages of your site are already in the search engines index and bring traffic, we do not recommend changing them, because the URL format is one of hundreds of factors that can affect the ranking of a particular site, and the influence of this factor is not a priority.
If there really is a need to replace the URL, for example, because of the risk of imposing sanctions (using spam construction, listing key phrases, etc.), do not forget to set up 301 redirects!
Experiment: how Yandex and Google consider keywords in a URL
The fact that in order to effectively promote websites you need to use CNC, today every SEO student knows, because all the labor bloggers talk about it, write in books and even talk at SEO conferences ... However, it’s worth a little deeper and ask “where does that come from? search engines take keywords from URLs into account when ranking? ”, in response you get something like“ if the URL is bold in the output, then the search engine understands the highlighted words, and therefore takes them into account when ranking ”... Do you feel the weak link in this thesis?

"Understands" is not equal to "takes into account"! You don’t have to go far for an example - meta name keywords. Do search engines understand the meaning of this tag, as well as the keywords that are listed in it? Undoubtedly. Does this tag have an impact? Unfortunately not. Perhaps the same is true of the keywords in the CNC?
Experiment
In order not to read the tea leaves, I conducted a small experiment. The purpose of the experiment is to check whether the site will be searched for keywords that are used in the URL, but which are not on the page.
A site was created on a new domain, some of the pages were in Latin (Russian words translated into English, Russian words in transliteration, abracadabra in Latin), and some in Cyrillic (Russian words written in Cyrillic, abracadabra in Cyrillic). Apart from the main one, it turned out 10 pages:
- URL of 1 word - Cyrillic (/ password.html)
- URL of 1 word - Latin translate (/parol.html)
- URL of 1 word - Latin translation (/password.html)
- URL of 1 word - Cyrillic-abracadabra (/ a., .Html)
- URL of 1 word - Latin abracadabra (/afafhqqawf.html)
- URL of 2 words - Cyrillic (/ online course.html)
- URL of 2 words - Latin translate (/ online-kurs.html)
- URL of 2 words - Latin translation (/online-course.html)
- URL of 2 words - Latin abracadabra (/afafhqqdwf-fedtmus.html)
- URL of 2 words - Cyrillic-abracadabra (/ aprosyvom- furtom.html)
The result of the experiment
After indexing the site in Yandex and Google, the following results were obtained.
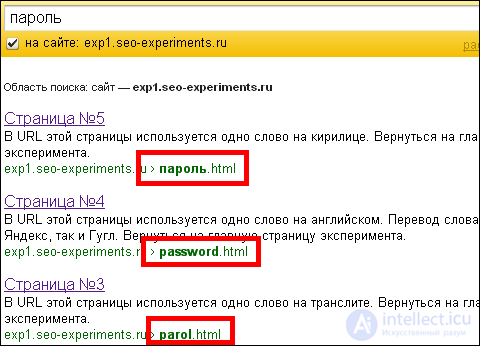
Search in Yandex with restriction on the domain
By the word “password” there were all 3 pages (Cyrillic, transliteration, translation), in the first place there is a page with Cyrillic, on the second translation, on the third transliteration:
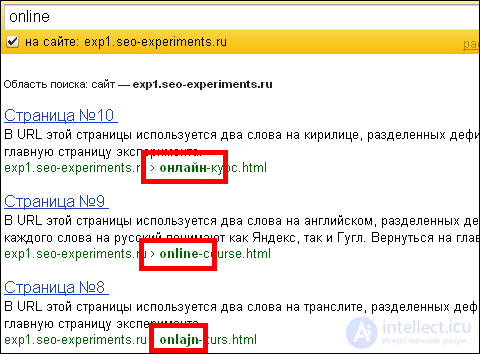
For the requests “online”, “course”, “online course”, “course online” all 3 relevant pages were found, each time the sequence was kept the same:
- Cyrillic;
- Transfer;
- Translit
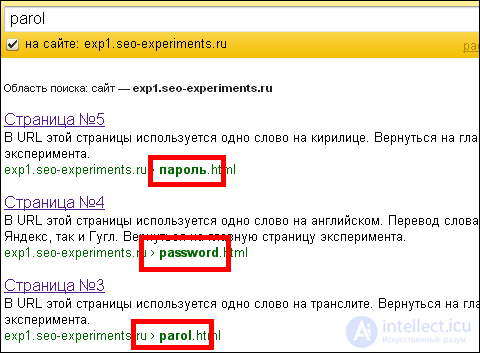
If you search not in the Russian word, but in English, then Yandex still finds all 3 documents, but the sequence in this case is different, and depends on the query. For example, the word “password” will first be translated, then Cyrillic, then translit:
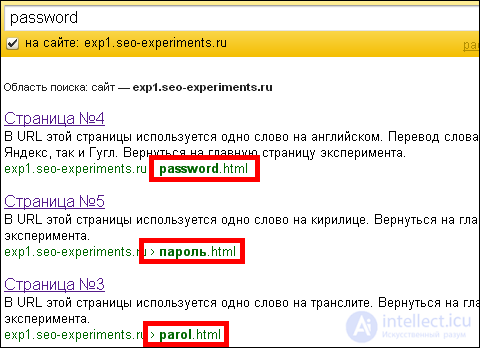
And according to the word “online”, Cyrillic will be the first, then English and at the end of the translation:
The funniest thing is that even if you look for the word on the translator “parol”, the “online” URL that contains the translite still turns out to be the most recent:
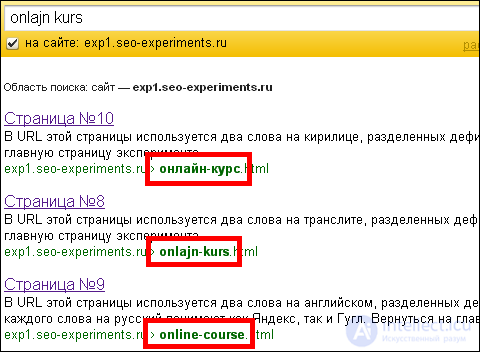
In the course of this experiment, another interesting feature was revealed - even if Yandex understands the meaning of a word, it does not always mark it bold in the URL. For example, on request “kurs”, all 3 documents are also found, but there are only two bold highlights:
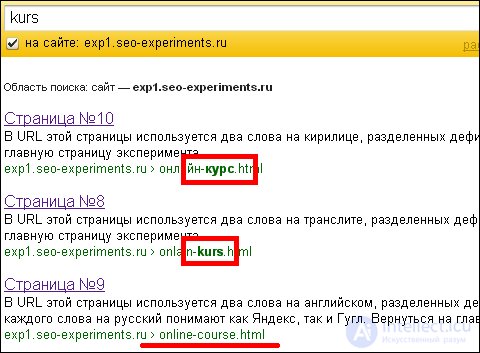
Although if you look for the phrase on the online kurs translate, the translation goes down to the 3rd place, the second is transliterated, and the first is still Cyrillic:
Search in Yandex without restrictions
Unfortunately, due to the limitation of 1000 results, I could not find the site in issuing Yandex for the queries I wrote about above. However, the site is wonderfully searched by abrocadabra:
- aenlshenopapkalom
- aenlshenopapkalom furasite
- afauoyugkjgdfgdfwf
- affhgdfhdfdsawf fedtoramus
Google search with domain restriction
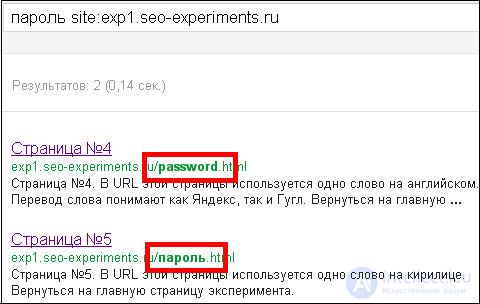
It turned out that Google does not like translit even more than Yandex. On request, the "password" in issuing only Cyrillic and translation, and in the first place is the translation:
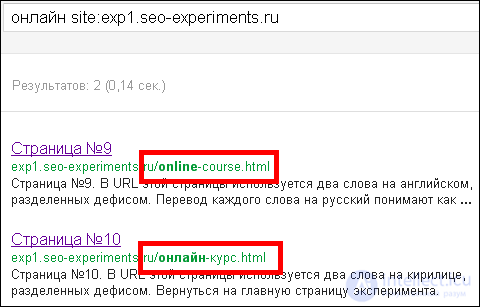
The same situation with the query "online":
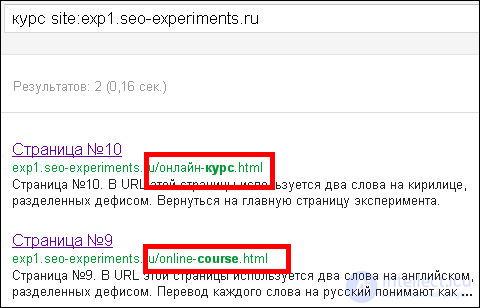
Although, for example, the query “course” comes first with a URL that contains a keyword in Cyrillic, and only then the translation:
Google still understands Google transliteration, but it seems to treat it very peculiarly. For example, on request “parol”, there is a translit in the issue (in the first place) and Cyrillic (in the second), but there is no translation. Understanding the meaning of the word in translit, Google offers to search for the word in Cyrillic:
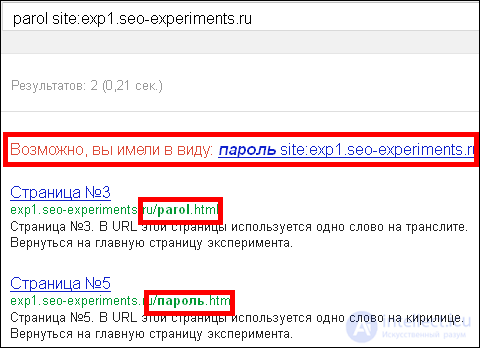
At the same time, Google understands far from all words, for example, for the query “kurs”, the Cyrillic URL was not found:
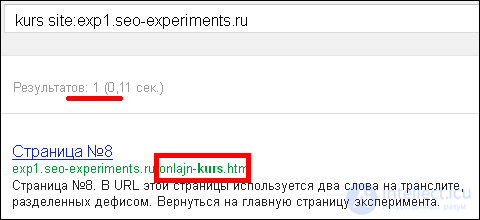
findings
- Cyrillic URL they rule;
- URLs that contain the translation also rule, but Yandex and Google should understand that this translation (but you should not forget that there are cases when the search engine understands the word in the URL, but does not select anything bold);
- URLs on transliteration somehow work in Yandex, but work very badly in Google.
Conclusion
Finally, another interesting thought. Recently, search engines have been paying more and more attention to the naturalness of the leaf anchor. If you simply buy links with direct entries, you can drive the site under the filter. True SEO specialists recommend buying bezankornye links, but many continue to be purchased in the old manner, not wanting to spend money on dilution.
Why am I doing all this? In the experiment described above, it is clearly shown that search engines find documents by words that are in the URL, but which are not in the text.Based on this observation, it can be assumed that if a link to the site is http://intellect.bond/key.html, then the reference key will be transmitted by the word “key”. It turns out that such bezankornye links are not at all bezankornye, so they can not only build up the mythical "trust", but also to promote the requests that are contained in the URL.
Have questions? Ask them in the comments!























Comments
To leave a comment
seo, smo, monetization, basics of internet marketing
Terms: seo, smo, monetization, basics of internet marketing