Lecture
If you believe the rumors, then we now live in something called Real -time web, the Internet in real time .
Now the users of the network generate so much content that this continuous stream of information is no longer comparable to a stream, and I would even say that it is a raging, wide, full-flowing river, and the search engine had a difficult task how to swallow it all without drowning.
Based on this, we can come to the conclusion that fresh content for search engines is becoming increasingly important .
We see how every day the indexation of new posts on blogs and social networks is faster.
Without a doubt, "freshness" is of great importance. But how does Google define it?
In addition to the date of entry into the index, are there any other factors that the search robot takes into account to determine the age of the page, perhaps some internal ones, such as dates in the content or in the URL address?
Let's try to determine it experimentally, I think it should be interesting.
I started my experiment with the simplest: I decided to change the URL of one of the pages of my blog, transforming it into a data format (in some blogs, this is the default address format).
I explain, for example, if the URL was:
www.mysite.com/topic-goes-here
... after the transformation, he became so ...
www.mysite.com/2039-09-01-topic-goes-here
I chose a new post that has not yet entered the index of search engines, but not so fresh as to attract external links (for the purity of the experiment, we need nothing). In order to track my post in the sickle, I chose three long key phrases. In the first part of the experiment, I did not stick the old URL with the new one. Without making 301 redirects, I wanted to "push" Google to index the page in a new way and update the cache. And now look at the graph of what happened:
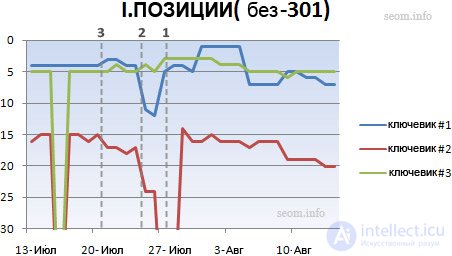
The curve is inverted to display low positions at the top, with one line for each search phrase.
Something strange happened here. Even after search robots indexed a new URL, this URL appeared in the SERPA on 3 different days with 3 key phrases (indicated by a gray dotted line).
Some positions fell before a new one appeared, some after that, until they stabilized on positions just below the original URLs. Surprisingly, one of the keywords that was in the first position, after changing the address, a 404-error entered the cache (which by itself is absolutely useless).
Naturally, a complete change of the URL without a 301 redirect looks weird and I lost all the reference weight that was transferred to this page (although it was a bit, but still pitiful).
I hope you learned a lesson from the first part of my experiment, so I decided to continue, this time I used a new blog post, but with a 301 redirect .
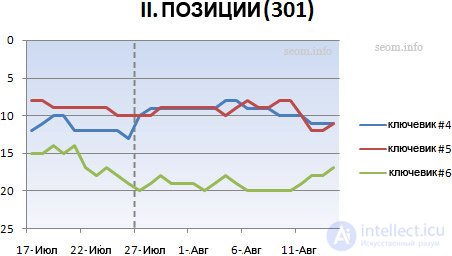
No wonder that search bots behaved better, all three keywords got into the CEPP in one day. Some keywords have lost their positions a bit, on the contrary, some jumped, but on average, the positions did not change much after gluing. Nothing encouraging for my theory of “freshness” based on URLs in a data format.
So, what have we learned from our little experiment on freshness?
I'm still not completely sure, but still I think we can draw some conclusions and my experiment was not in vain.
So :
If you are going to change all your URLs in order to mislead Google and he decided that you have new, fresh posts. My advice to you is not to do this.
When I conducted my SEO experiment , I had certain reasons in its first part not to use 301 redirects. When you change an important URL, always use this tool. The first schedule can serve as a good example of what happens if you do not.
Even if you had to change your URLs for some very important reason and you glued the addresses to 301 with a redirect, some short-term consequences of such actions will follow. It is possible that the positions in the SERPA will fall; you should not expect that with the new address you will start from the same positions on which you ended up with the old address. Changing the structure of your URLs is always a lot of work - but sometimes it just needs to be done, in such cases you need to seriously approach this business, and not as using any regular SEO chips.
How often do you use a 301 redirect?
We always expect that when pasting addresses with a 301 redirect, 1-10% of the reference weight is lost .
I also hold the opinion that it is very difficult to work with 301 on Google, despite this several years ago some of my friends managed to find a “hole”, which they successfully exploited.
: with reference to Yandex, it can be said that the only difficulty when working with a 301 redirect is the period during which the mirror man will go through and glue together the necessary addresses. You should not rely on fast gluing, you need to take a period of 3 months as a basis, although it is possible and faster if you are lucky Another complication may not be a pleasant surprise in the form of a glitch, but this already applies to working with mirrors, and not to the topic of this post.
Attention: The author specially checked in practice all his theories on his own website that you would not do these experiments on your websites.
Comments
To leave a comment
seo, smo, monetization, basics of internet marketing
Terms: seo, smo, monetization, basics of internet marketing