Lecture
In philosophy, form is the structure of some kind of content. The form of training organization refers to the external side of the learning process, which is related to the number of students, time and place, as well as the order of its implementation [I. F. Kharlamov].
In the history of pedagogy, there are two main forms of organization of training: individual-group and class-time. The system of individual learning became widespread in the early stages of the development of society, when the teacher was engaged with one student, as a rule, his successor. Gradually, individual group learning emerged when the teacher was engaged with a group of 10-15 students. Training in the group was also carried out individually, therefore in the group there were students of different ages, different levels of training. Dates of study, beginning and end of classes were also individual.
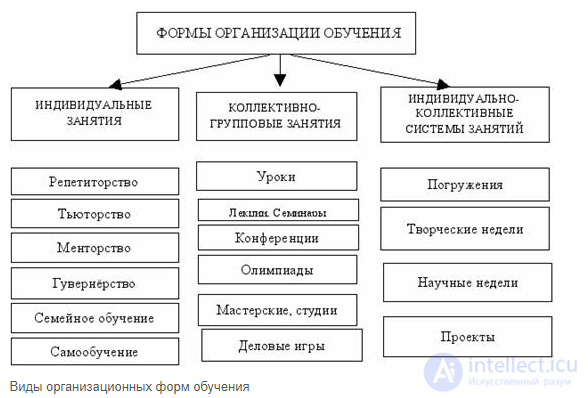
In the Middle Ages, in connection with the increase in the number of students, it became necessary to introduce a new form of organization of education. The group form of education has spread. She found her complete solution in the class-study system of training developed and theoretically substantiated by Ya. A. Komensky. It assumes the presence in the group of a constant composition of students of the same age; permanent place and duration of classes, stable schedule of classes.
Later on, other forms of organization of education appeared in didactics, aimed at improving the class-lesson system. So, in the XVIII century. in England, a Bell-Lancaster system was spread , covering 600 and more students of different ages and levels of training at the same time. Its essence was that the teacher taught older and more successful students - monitors, who in turn taught the others.
The Dalton Plan (workshop system) is another form of education that spread at the beginning of the 20th century in the USA. Instead of traditional classes, pupils were engaged in the subject workshops on an individual assignment received from the teacher. The training went according to a free schedule on the basis of independent work, after which the student reported to the teacher. In Russia, this form served as the basis for the development in the 20s of the XX century. Brigade-laboratory form of training, combining teamwork with the brigade and individual.
Despite the existing variety of forms of organization of education, the class-lesson system remains the leading form. Its benefits include: having a strict organizational structure; profitability, since one teacher simultaneously works with a large group of students; the possibility of mutual learning through collective activities; providing education and development of students. At the same time, this form is not without flaws, the main among them being the orientation towards the “average” student, limited opportunities for individualizing education.
The main component of the class-lesson system is a lesson. It reflects all the advantages of this system. A lesson is a form of organization of the pedagogical process in which the teacher, for a precisely set time, leads the collective cognitive and other activities of the permanent group of students (class) taking into account the characteristics of each of them, using the types, means and methods of work so that students master the basics the subject studied directly in the learning process, as well as for the education and development of cognitive abilities and spiritual forces of schoolchildren. The presence of all signs distinguishes the lesson from other organizational forms and constitutes its essence.
In each lesson, you can select its main parts, which in various combinations make up the structure of lessons. The main parts of the lesson are: checking homework and interviewing students; study of new material; primary consolidation and systematization of new material; homework. Depending on the ratio of these parts, types of lessons are distinguished (according to B. P. Esipov): lessons on acquaintance with new material (messages of new knowledge); lessons consolidate new knowledge; skills development lessons; lessons test knowledge, skills and abilities (checklists); combined lessons.
In addition to the lesson as the main form of study in practice, widely used are additional forms, which include excursions, homework, extra classes. Recently there are electives, interest clubs, which serve the tasks of individualizing learning and developing students' interests.
Comments
To leave a comment
Pedagogy and didactics
Terms: Pedagogy and didactics