Lecture
The scheme of experiments on subtractive color equalization is shown in Fig. 3.3.3. Light with spectral density 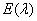 consistently passes through three filters - cyan, magenta and yellow. The spectral absorption curve of each dye depends on its concentration. It should be noted that the absorption curves of the dyes used in practice change in a nonlinear manner as their concentrations change.
consistently passes through three filters - cyan, magenta and yellow. The spectral absorption curve of each dye depends on its concentration. It should be noted that the absorption curves of the dyes used in practice change in a nonlinear manner as their concentrations change.
In the first stage of the subtractive adjustment process, the dye concentrations of the three filters change until a subjective adjustment of the reference white color is achieved. 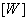 . These concentrations are equalizing values.
. These concentrations are equalizing values. 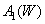 ,
, 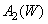 ,
, 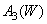 . Concentrations are then adjusted to equalize the desired color.
. Concentrations are then adjusted to equalize the desired color. 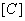 . Found concentrations - equalizing values
. Found concentrations - equalizing values 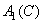 ,
, 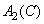 ,
, 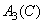 - used when calculating coordinates
- used when calculating coordinates 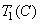 ,
, 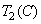 ,
, 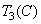 according to the relation (3.3.1). Obviously, there is no fundamental difference between additive and subtractive color equalization. In the subtractive system, the yellow dye acts as a variable absorber of blue light, i.e., controls its intensity. In the same way, the magenta filter controls the green, and the cyan - by the red light. These filters are broadband and transmit a lot of light. Therefore, they are more convenient to use in subtractive systems than narrowband red, green and blue filters.
according to the relation (3.3.1). Obviously, there is no fundamental difference between additive and subtractive color equalization. In the subtractive system, the yellow dye acts as a variable absorber of blue light, i.e., controls its intensity. In the same way, the magenta filter controls the green, and the cyan - by the red light. These filters are broadband and transmit a lot of light. Therefore, they are more convenient to use in subtractive systems than narrowband red, green and blue filters.

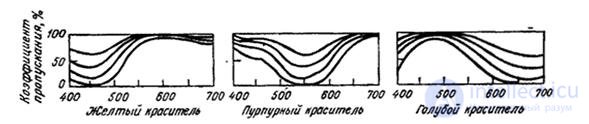
Fig. 3.3.3. Subtractive color adjustment.
Conventional dyes do not have a wide range of density changes. In order to increase the contrast of the reproduced image, a fourth filter layer — neutral gray — is often introduced into the printing industry. Subtractive reproduction of colors with real dyes with overlapping absorption curves is discussed in Chap. sixteen.
Comments
To leave a comment
Digital image processing
Terms: Digital image processing