Lecture
In a real image sampling system, the sampling grid has finite dimensions, the width of the sampling pulses is noticeably different from zero, and the image samples can be taken with insufficient frequency. Consider the consequences of such non-ideal discretization.
The analysis will be based on the typical image scanning system shown in Fig. 4.2.1. The original image, represented as a transparency, is scanned with a hopping thin light beam. The light passing through the slide is collected by a condenser lens and directed to the photosensitive surface of the photodetector. The electrical signal from the output of the photodetector is integrated for a period of time during which the light beam illuminates the given image element. During the analysis, we will assume that in the process of sampling additional noise in the signal is not made. Therefore, the results of the previous section relating to the discretization of noisy images can be easily combined with the conclusions of this section. It should also be noted that the following analysis easily extends to a wide class of real systems. image sampling .
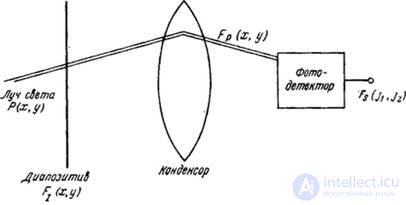
Fig. 4.2.1. Typical image scanning system.
In a real image sampling system, the sampling grid has finite dimensions, the width of the sampling pulses is noticeably different from zero, and the image samples can be taken with insufficient frequency. Consider the consequences of such non-ideal discretization.
The analysis will be based on the typical image scanning system shown in Fig. 4.2.1. The original image, represented as a transparency, is scanned with a hopping thin light beam. The light passing through the slide is collected by a condenser lens and directed to the photosensitive surface of the photodetector. The electrical signal from the output of the photodetector is integrated for a period of time during which the light beam illuminates the given image element. During the analysis, we will assume that in the process of sampling additional noise in the signal is not made. Therefore, the results of the previous section relating to the discretization of noisy images can be easily combined with the conclusions of this section. It should also be noted that the analysis below is easily extended to a wide class of real image sampling systems.

Fig. 4.2.1. Typical image scanning system.
Comments
To leave a comment
Digital image processing
Terms: Digital image processing