Lecture
Colorimetry is the science of measuring colors. For the measurement of colors using different coordinate systems.
From the eighth axiom of Grassmann it follows that the color 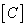 can be equalized with a mixture of three primary colors
can be equalized with a mixture of three primary colors 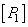 ,
, 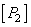 and
and 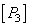 i.e.
i.e.
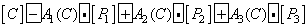 , (3.4.1)
, (3.4.1)
Where 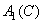 ,
, 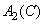 ,
, 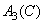 - equalizing color values
- equalizing color values 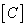 . Since the intensities of incoherent light sources add up linearly, the spectral density of the mixture is equal to the sum of the spectral densities of its components. According to (3.4.1), the spectral density
. Since the intensities of incoherent light sources add up linearly, the spectral density of the mixture is equal to the sum of the spectral densities of its components. According to (3.4.1), the spectral density 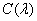 can be replaced by the equivalent spectral density of the mixture of primary colors, i.e.
can be replaced by the equivalent spectral density of the mixture of primary colors, i.e.
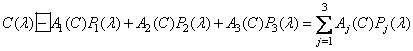 , (3.4.2)
, (3.4.2)
Where 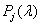 primary spectral density
primary spectral density 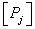 . The relation (3.4.2) has a simple meaning: spectral densities connected by an equivalence operator
. The relation (3.4.2) has a simple meaning: spectral densities connected by an equivalence operator  cause the same color sensation. Vocalorimetry uses color coordinates that are equal to
cause the same color sensation. Vocalorimetry uses color coordinates that are equal to
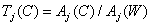 , (3.4.3)
, (3.4.3)
Where 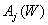 equalizing the value of the reference white. Substituting expression (3.4.3) into (3.4.2), we obtain
equalizing the value of the reference white. Substituting expression (3.4.3) into (3.4.2), we obtain
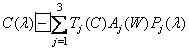 . (3.4.4)
. (3.4.4)
From the fourth axiom of Grassmann it follows that the brightness of the color 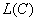 equal to the sum of the brightness of its main components. Consequently,
equal to the sum of the brightness of its main components. Consequently,
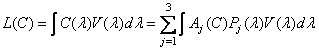 , (3.4.5a)
, (3.4.5a)
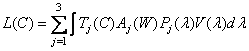 , (3.4.5b)
, (3.4.5b)
Where 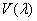 - relative luminous efficiency. Relations (3.4.4) and (3.4.5) are the quantitative basis of colorimetry.
- relative luminous efficiency. Relations (3.4.4) and (3.4.5) are the quantitative basis of colorimetry.
Comments
To leave a comment
Digital image processing
Terms: Digital image processing