Lecture
The distribution of energy of the source of light radiation by spatial coordinates 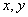 time
time 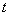 and wavelengths
and wavelengths 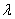 described by function
described by function 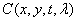 . The radiation energy is proportional to the square of the amplitude of the electric field and therefore represents a real positive value. In imaging systems, the maximum brightness of the image is limited due to saturation of the photosensitive film or overheating of the phosphor of the kinescope. Consequently,
. The radiation energy is proportional to the square of the amplitude of the electric field and therefore represents a real positive value. In imaging systems, the maximum brightness of the image is limited due to saturation of the photosensitive film or overheating of the phosphor of the kinescope. Consequently,
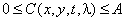 (1.1.1)
(1.1.1)
Where 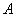 - The maximum brightness of the image. The dimensions of the image are limited by the forming system and the environment in which it is recorded. For the sake of simplicity, we will assume that all images are nonzero only in a rectangular area for which
- The maximum brightness of the image. The dimensions of the image are limited by the forming system and the environment in which it is recorded. For the sake of simplicity, we will assume that all images are nonzero only in a rectangular area for which
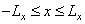 (1.1.2a)
(1.1.2a)
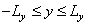 (1.1.2b)
(1.1.2b)
The image is observed during a finite period of time, i.e.
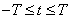 (1.1.2b)
(1.1.2b)
Thus, the magnitude 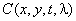 is a bounded function of four bounded variables. We will consider this function continuous in the domain of its definition.
is a bounded function of four bounded variables. We will consider this function continuous in the domain of its definition.
The feeling of lightness that occurs in the human visual system is usually determined by the instantaneous brightness of the light field, i.e.
 (1. 1.3),
(1. 1.3),
Where 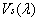 - spectral sensitivity of human vision. Color sensations can be described by a set of so-called flowering coordinates, proportional to the intensities of red, green and blue, the mixture of which gives a given color. For an arbitrary red-green-blue coordinate system, the current values of the color coordinates are
- spectral sensitivity of human vision. Color sensations can be described by a set of so-called flowering coordinates, proportional to the intensities of red, green and blue, the mixture of which gives a given color. For an arbitrary red-green-blue coordinate system, the current values of the color coordinates are
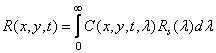 (1.1.4a)
(1.1.4a)
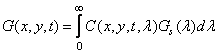 (1.1.4b)
(1.1.4b)
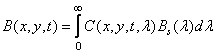 (1.1.4b)
(1.1.4b)
Where 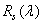 ,
, 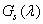 ,
, 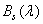 - specific coordinates for a set of primary colors - red, green and blue, equal to the coordinates of the color of monochromatic radiation of unit intensity with a wavelength
- specific coordinates for a set of primary colors - red, green and blue, equal to the coordinates of the color of monochromatic radiation of unit intensity with a wavelength 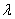 . In the multispectral image systems for
. In the multispectral image systems for 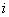 spectral zone is described by the expression
spectral zone is described by the expression
 (1.1.5),
(1.1.5),
Where 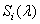 - spectral sensitivity
- spectral sensitivity 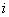 th sensor.
th sensor.
For simplicity, we will in all cases describe the image formed by some physical system using the function 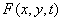 . For monochrome system function
. For monochrome system function 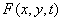 represents the distribution of brightness or some other physical quantity associated with brightness. For color reproduction system
represents the distribution of brightness or some other physical quantity associated with brightness. For color reproduction system 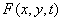 there is one of the color coordinates. Function
there is one of the color coordinates. Function 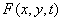 It is also used to describe other fields, for example, the time-varying spatial distribution of the noise of a video sensor.
It is also used to describe other fields, for example, the time-varying spatial distribution of the noise of a video sensor.
In accordance with the usual definition of the average value of a one-dimensional signal, the time average brightness of the image at a given point 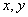 defined as
defined as
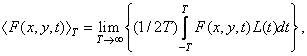 (1.1.6)
(1.1.6)
Where 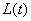 - temporary weight function. The spatial average brightness at the moment of time is determined similarly.
- temporary weight function. The spatial average brightness at the moment of time is determined similarly. 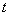 :
:
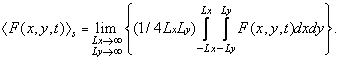 (1.1.7)
(1.1.7)
In many image reproduction systems, such as projection devices, the image does not change over time and the variable 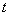 may be omitted. In systems of another type, such as cinematic, the argument
may be omitted. In systems of another type, such as cinematic, the argument 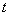 varies discretely. Further argument
varies discretely. Further argument 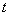 the function that captures the image will usually be omitted.
the function that captures the image will usually be omitted.
Comments
To leave a comment
Digital image processing
Terms: Digital image processing