Lecture
Representatives of classical management schools analyzed primarily internal factors of the organization * . External factors remained out of their sight. However, any organization exists in the external environment (suppliers, competitors, consumers, etc.). The external environment lives constantly, changes and has a great influence on the organization. Many authors in the field of management theory and practice note that until approximately 1975, the external environment was relatively stable and calm. Before this period, the American management model worked effectively. It had the following characteristics:
From the middle of the 70s to the beginning of the 80s, the situation became more complicated. Global changes are beginning to take place in the environment:
In managerial thought, the idea of strengthening the influence of the external environment on the organization’s activities arises and then strengthens. Moreover, “the external environment of an organization is increasingly becoming a source of problems for modern managers. In fact, the leaders of the most important organizations for society have been forced to focus on the rapidly changing environment and its effects on the internal structure of organizations”. [].
Almost all environmental factors are uncontrolled by the organization and its services. The best plan can fail because of the negative effects of uncontrolled factors. At the same time, it should be noted that organizations can not only adapt to a changing environment, but also to a certain extent influence it.
When analyzing external factors, two types of them are usually distinguished: direct influence factors, sometimes called the immediate environment, and indirect influence factors, sometimes called the general environment.
Factors of direct impact include those that directly affect the operations of the organization and are directly affected by the operations of the organization.
The organization and its environment can be represented in the following form (see. Fig. 2.3). Briefly describe the external environment of direct impact on the organization.
1. Suppliers . This category of external environment usually includes:
a) suppliers of materials, energy, equipment and components, i.e., there is a dependence on prices, terms, rhythm, quality, etc. And this dependence has recently increased with the deepening division of labor and the development of cooperation. Firms are increasingly focused on the preferential purchase of component parts from partners, and the firms themselves perform only certain operations, and this is typical of both production and service companies. Therefore, we can talk about the increasing gain of their dependence on suppliers in the future. At the same time, there are changes in the relations between purchasers and suppliers, based on the Japanese subcontracting system, the organization of an efficient supply chain. At the same time, additional powers and responsibilities are transferred to suppliers in both the design and production areas, which makes it possible to speak of the management of suppliers;
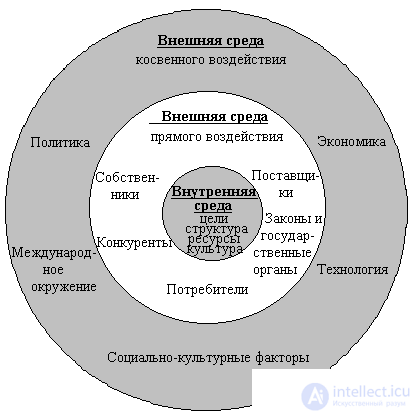
Fig. 2.3. Organization and its environment
b) providers of capital and financial services, here there is a dependence on the volumes, terms of loans and mutual settlements, insurance services, etc. Usually, the following investors are singled out: banks, insurance companies, other financial and non-financial companies, programs of government agencies for the presentation of loans, shareholders and private individuals.
Large companies seek to ensure their financial independence by serving a high level of profitability and to serve themselves as banks and even finance other firms (sometimes this results in the creation of their own banks). An example would be Avtovazbank, established by the Volga Automobile Plant, Hermes Bank, established by Hermes-Soyuz, etc. Medium and small firms depend on external sources of financing and are forced to pay high interest on loans. Sometimes fluctuations in interest rates force a change in the orientation of the firm’s activities. For example, in the USA, when bank interest jumped sharply, construction firms (depending on debt financing) were forced to switch from building individual houses to building multi-apartment buildings;
c) labor resources - that is, the dependence of the company on the market, first of all on qualified personnel, on wage level requirements * , etc. Despite the unemployment peculiar to a market economy, there is a constant shortage of highly qualified personnel in all areas. The shortage of specialists and the increased requirements for the level of qualification of personnel force companies to either look for such personnel, or to invest heavily in their training, in job security, that is, to move from primarily short-term to long-term employment, to social security.
The factor "labor resources" is closely related to issues that arise in organizations with trade unions, with their demands on the level of wages, social protection and working conditions. Moreover, in different countries, these relationships are manifested in different ways. For example, in the USA, the management of firms traditionally clashed with trade unions, while in Japan they, as a rule, successfully cooperate. In Russia at the present time the edge of the demands of the trade unions is directed towards the government, however, as the privatization processes develop, we should expect their increased attention directly to the leadership of the company and organizations.
2. Laws and government agencies. Each organization has a specific legal status, which determines how it can conduct business, what rights it has and what responsibilities it has before the state and local governments. As you know, the state in a market economy has on organizations as an indirect influence, primarily through the tax system, state property and the budget, and directly through legislative acts. So, for example, high tax rates significantly limit the activity of firms, their investment opportunities and push to the concealment of income. On the contrary, a reduction in tax rates contributes to attracting capital, leads to a revival of business activity. And thus, with the help of taxes, the state can manage the development of the necessary directions in the economy.
3. Consumers - this is a factor at the modern marketing stage of management development is considered as its basis. Consumers decide whether the firm will be able to recover its costs, make a profit and, therefore, get its development. All the variety of external factors is reflected in the consumer and through him affects the organization, its goals and strategy * . In modern conditions, various associations and associations of consumers, which have an impact not only on demand, but also on the image of firms, become important. It is necessary to take into account factors affecting consumer behavior, their demand. Moreover, it is necessary not only to predict, but also to influence, “create” the consumer. It is sometimes difficult to identify the consumer, that is, to get a clear idea of the structure of needs that must be met, especially if we are talking about commercial structures that are becoming increasingly widespread. Manufacturers of industrial products usually dealt with final consumers and producers of fixed capital goods. But now they are faced with a new situation. Since their products, by the method of sale, acquire the character of consumer goods, dealers (agents and distributors) come to the fore in the sale of both consumer goods and industrial products. If in this case there is a need to study the structure of requests of new consumers, then dealers, as a rule, are engaged in this.
4. Competitors. In many cases, not consumers, but competitors determine which product and at what price it can be sold. Moreover, the loss of, for example, a 10% market share usually entails a 5–8% decrease in the rate of profit.
Underestimation of competitors and reassessment of markets lead even the largest companies to significant losses and crises. Along with the struggle for markets, the competitive struggle for commodity markets, labor, capital, the right to use scientific and technical innovations is increasing.
The modern development of science and technology in the conditions of scientific and technological revolution significantly sharpened the competition between firms. The most important condition for the prosperity of the company is its continuous improvement and, above all, on the basis of modern achievements of science and technology. Scientific discovery or a fundamentally new product or service can take the company to the top of success.
At the same time, it should be noted that competition sometimes pushes firms to create different types of agreements between them from market division to cooperation between competitors.
5. Owners. One of the main influences on the organization is provided by the form of ownership and the property representatives themselves - the owners. This factor, however, like the others, is closely intertwined with the rest, both of the internal environment and the external environment of the organization. With the diffusion of capital, the development of share capital, an extensive stratum of owners is formed, which have a significant impact on the development of organizations.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management