Lecture
In the engineering design of workshops and sites the following work is performed:
Calculation of needs in the main technological equipment. Determine the required composition of equipment in the context of the site as a whole with the calculation of load factors. The estimated number of machines S pj for the j-th interchangeable groups of equipment according to the nomenclature list of parts d assigned to the site (line) is determined by the formula:
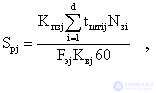
where K pzj - coefficient taking into account the time spent on preparatory and final * work (K pzj = 1.01 - 1.2); t pcsij - the complexity of performing a set of operations for processing the i-th part on the j-th group of equipment, min; N zi - annual launch program of the i-th part, pcs .; K вj - coefficient taking into account the over-fulfillment of the norm of the task (K вj = 1.01 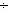 1,2); F ej is the effective annual fund for the work of equipment of the j-th group.
1,2); F ej is the effective annual fund for the work of equipment of the j-th group.
In turn
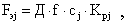
where D is the number of working days per year; f - work shift duration, hours; c j - shift mode for the j-th equipment group (c j = 1, 2, 3); K pj - the planned loss rate for repair time for the j-th equipment group (K pj = 0.85 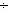 0.95).
0.95).
Set the equipment groups the required number of machines S pj by the corresponding rounding of the obtained value of S pj to the whole. At the same time, an overload of no more than 10% per one machine is allowed. For example, when S p = 1,1 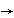 S n = 1; S p = 1,2
S n = 1; S p = 1,2 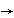 S n = 2.
S n = 2.
Calculate the average load factors of the equipment for the groups K sj and the section (lines) as a whole K for (l) by dependencies:
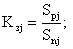
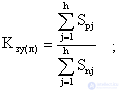
After the calculations, it is necessary to substantiate a rational number of equal in terms of the quantitative composition of the equipment and the norms of controllability of the shops and individual sections of the shop.
The formation of sections occurs by successive summation (cumulative) of the values of K gij over groups of parts until the condition is satisfied:
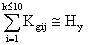
where H y - the rate of control * for the master, expressed by the number of jobs it serves (15 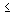 H y
H y 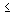 35 pieces of equipment for one master). Selecting the first section, the same procedure on the basis of the remaining set of details determines the subsequent sections of the workshop.
35 pieces of equipment for one master). Selecting the first section, the same procedure on the basis of the remaining set of details determines the subsequent sections of the workshop.
If the value of K gijk is much higher than 150, it is recommended to create two or more of the same type of workshops. (In the construction part of the project, these workshops can be located in the same building or separately.)
The results of the calculations are the formation of the structure of the main production with the definition of their specialization.
Calculation of the required production space. Under the production area refers to the territory of the site, shop, which carried out the production processes for the manufacture of parts.
The simplest practical method for calculating production areas is the method of using construction norms and standards for design * .
The essence of this method is to use the values of specific areas (S beats) per worker or per unit of process equipment.
Using reference standards for PS design, the required areas are determined by the formulas:
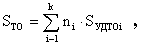
where S T.O. - the required area for technologically equipped workplaces; n i - the number of technological equipment of the i-th size group; S UDTOi - specific area for technological equipment of the i-th size group; k - the number of dimensional type-groups.
Any process equipment with an area in terms of the corresponding size group is included in the size group.
It should also be noted that the norms of distances between equipment are included in the specific area; between equipment, building and facilities; between the passage (passage) and the working area. These standards take into account safety requirements, maintenance of workplaces and the possibility of repair work.
Calculation of the required area for other categories of workers:
S p = H p · S beats r
where S p - the required area for workers; H p - the number of employees; S beats p - specific area per worker (S beats p = 4 - 4.5 m 2 per worker and S beats p = 4.5 - 6 m 2 per working place * , having additional equipment, such as: quacks , special cabinets, copying equipment, etc.).
The total required area of subdivisions is determined by the standard ratio of the use of space.
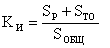
Normative K И = 0.5 - 0.7.
From here
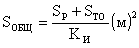
Calculation of the number of employees on the sites and in the shop. Calculation of the need for basic production workers. The number of main production workers largely depends on the forms of work organization in the workplace.
In simplified form, the number of main workers is determined by the formula:
P o = P ST + P R.P.
where: Р СТ - machine workers; R. R.R. - Workers serving handmade sites (locksmiths, fitters, assemblers, etc.).
The calculation of the number of workers-machine-workers. It is carried out according to the formula:
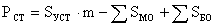
where: S УСТ - the fixed amount of equipment; m is the number of shifts in equipment operation; S MO - the number of groups of workplaces with a multi-machine service; S BO - the number of jobs with brigade form of service (forging equipment, aggregate, smelting, etc.).
The number of main production jobs manual work is determined by the formula:
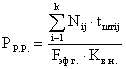
where N ij - the volume of production for the i-th parts, for the j-th manual work; t pieceij - laboriousness on the relevant indicators; F ef.g. - effective annual fund of the time of work of one worker; k - nomenclature list; K vn - the rate of implementation of the norms (K vn = 1.0 - 1.2).
Determining the number of auxiliary workers, MOS, engineers, AUP.
In the practice of design are often used aggregated standards of the number of these categories of the number of main workers.
Thus, the number of auxiliary workers is taken for machine building and instrument-making enterprises in relation to the main ones as 1: 1.
The number of MOS - 1.0 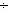 1.5% of the main and auxiliary workers.
1.5% of the main and auxiliary workers.
The number of engineers, depending on the type and complexity of production - 20 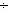 40% of the total number of production workers.
40% of the total number of production workers.
AUP is accepted from all categories of workers as 20 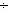 25% of their numbers.
25% of their numbers.
Determine the area required to accommodate auxiliary areas, farms and other services of the shop. The basis for the calculation of these parameters is the structure and capacity of the main production department. In this case, the norms and standards for the design of these services are used, depending on the capacity of the main production.
Development of layouts. The final stage of the design work is the development of sites and the shop as a whole.
The layouts are production facilities made to scale, with rational placement of equipment and other facilities with observance of the norms of distances between equipment, equipment and building structures that meet the requirements of straightness and taking into account labor protection rules. An embodiment of the planning is given in the appendix.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management