Lecture
The most important factor predetermining the forms and methods of organization, planning and management at the enterprise is the type of production.
Under the type of production refers to the classification characteristics of production on the latitude of the nomenclature, volume, regularity and stability of the release of products. From an organizational and economic point of view, the type of production is a generalizing characteristic of the production process, expressing the nature and number of internal relations between the main elements of the production process and the degree of consistency of production conditions at workplaces depending on them.
The main quantitative characteristic of the type of production is the coefficient of consolidation of operations K z.o , determined by the ratio of the number of all the various parts of the operations performed in the production system during the month, D o to the calculated number of work places S p , ie
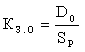
As you can see, K zo shows the average number of part-operations performed on one workplace of the production system (site, workshop) during the month. It characterizes the degree of stability of production processes in the workplace.
The estimated number of jobs loaded on the site (workshop) is determined by the ratio of the labor intensity of the production volume required for output in the planned period (year, quarter, month) to the effective time base of the equipment unit in this period, i.e.
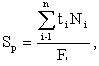
where t i - the complexity of manufacturing units of the i- th product, h; N i - the volume of production of the i- th product in the planned period, pcs .; n is the number of types of products; F e - the effective Fund of working time of the equipment in the planning period, h.
The value of K zo for the considered production system in combination with the qualitative features of the production process, such as regularity (repeatability) and stability (continuity) of processes at workplaces, characterizes the type of production.
There are three main types of production: mass, serial and unit.
Mass production is characterized by the following distinctive features:
Narrow nomenclature and large volumes of products, continuously manufactured for a long time.
Each workplace * is loaded by performing one part-operation, i.e. K zo = 1.
For each operation, the volume of work performed and the effective working time fund are related by inequality of the form:
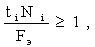
Full stability of the working conditions at workplaces, which allows: narrowly specializing workplaces and equipping them with special high-performance equipment; establish exact standards for all costs; carry out thorough technical preparation of production; allocate the production of items on interrelated chains of workplaces (production lines); ensure a high degree of parallelism, continuity and rhythm of production.
As a result of these advantages, the highest technical and economic indicators of production are achieved: high labor productivity; low production costs; the shortest production cycle; the minimum amount of work in progress and the binding of working capital.
Mass production has the following distinguishing features:
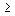 2. Since here the amount of work t i N i < F e for each item-operation, in order to achieve full workplace loading, it is necessary to assign to him the execution of several detail-operations D o in such a way that the condition
2. Since here the amount of work t i N i < F e for each item-operation, in order to achieve full workplace loading, it is necessary to assign to him the execution of several detail-operations D o in such a way that the condition 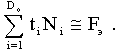
There are three types of mass production: large-scale - K zo = 2 - 4 (according to its characteristics, to mass); medium lot - K z.o = 5 - 22; small-scale - K z.o = 23 - 44. A distinctive feature of small-scale production is the irregular, episodic frequency of product release through long (previously unknown) periods of time with single or small volumes of output. Therefore, small-scale production of the nature of the organization to the unit.
Unit production is characterized by the following features:
The type of production * of the primary production units (plots) is determined by analyzing the calculated values of K z.o. and quality characteristics of stability and repeatability of production of products (parts). The type of production of a workshop is established according to similar criteria for its leading sections, and enterprises - according to the type of production of leading production workshops. However, in relation to even parts of one product in different workshops and in different parts of the plant, several types of production can be represented. This is determined, as has been shown, by a combination of the quantities produced by parts of the products and the labor intensity of their manufacture.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management