Lecture
The basis of the production process is labor - appropriate human activity.
The labor process is the process of an employee's influence on the object of labor in order to manufacture products or perform work, accompanied by the costs of physical and nervous energy of a person.
With the development of technology and technology in the content of labor of workers, significant changes occur: the direct physical impact on the object of labor decreases, the functions of observation, management, etc. become predominant.
The set of interrelated labor and natural processes aimed at the manufacture of products is called the production process. The production process * consists of process and transport control and product testing. Thus, the labor process is part of the production process.
The labor process * combines different in nature and content of work. The degree of dismemberment of the labor process depends on many factors: the use of technology, technology, work organization, etc. Work on the improvement of the labor process requires its specification, i.e. partitions into components.
All labor processes by the nature of the object and product of labor are divided into material-energy and informational. The first are characteristic for workers, the second - for employees. Further differentiation of labor processes is based on their functions. At present, it is customary to divide work processes into main and auxiliary, and accordingly also workers.
The main ones include workers' workshops directly involved in the production of this enterprise, to the subsidiary ones - all the workers of the auxiliary and main workshops engaged in servicing the equipment (repairmen, order pickers, etc.).
According to the degree of human participation in the impact on the object of labor, labor processes are divided into manual * , machine-manual * , machine * and automated * .
Manual processes are those in which workers act on the object of labor without the use of additional mechanisms or using hand tools.
To machine-manual include processes in which the impact on the object of labor is done through mechanisms, but there are also manual work.
With machine processes, the whole process is carried out without the physical effort of the worker, and the installation, removal of the part and control with the help of the worker.
With the automatic process, the worker only controls the work.
Recently, the third sign of the classification of work processes - organizational is increasingly being added. According to it, labor processes are divided into:
The correctness of attributing the labor process to a separate classification group is mandatory for their organization. The classification of work processes is given in table 8.2.
T a b i c a 8. 2
Classification of work processes.
Classification features | Process classes |
The nature of the subject and product of labor | Substance-energy (labor processes of workers). Information (employee work processes) |
Functions | Labor processes of workers employed:
Employee labor processes:
|
| The participation of workers in the impact on the subject of labor (level of automation of labor) | Hand held |
The division and cooperation of labor in the enterprise. The level of development of the productive forces of society is more clearly manifested in the development of the division of labor. In this regard, the social division of labor as a socio-economic category is inherent in all socio-economic formations, and its form and importance are essential.
In engineering within the enterprise, there are three main forms of the division of labor: functional, technological and classification [1].
Functional determines the relationship of workers to the production process, with it all production processes are divided into groups:
The most important direction of improving the division of labor is the establishment of a rational number of groups of workers in the direction of increasing the number of core workers .
The technological division of labor is the operational division of labor. This requires compliance with the following conditions:
The operational division of labor is the basis of line production and has its advantages. However, the excessive fragmentation of technological processes into the simplest operations impoverishes their content and enhances its monotony.
Labor cooperation in an enterprise is expressed in the form of a union of workers for joint and systematic participation in a single or in different, but interrelated labor processes. Types of cooperation of labor depend on the specialization of workshops, sites and organization of the production process. The three main forms of the division of labor correspond to three forms of labor cooperation.
The cooperation of labor of workers within the enterprise is carried out in the form of interdepartmental, intrashop and intraparty cooperation.
Interdepartmental cooperation is based on the division of the production process between individual workshops and is aimed at ensuring the systematic participation of these workshops in joint production processes.
Intrashop cooperation is the relationship between sites, work teams, workers.
Intra-area cooperation is expressed in production links between individual workers or teams within the site.
The most characteristic form of intra-cooperation cooperation is the formation of production brigades.
The organization of work processes is a system of measures aimed at ensuring the rational functioning of living labor in order to increase its productivity with the effective use of the means of production and the creation of the most favorable working conditions.
Forms of the organization of work processes. The organizational forms of work processes include: brigade, the combination of professions, multi-station service.
A systematic transition to the brigade form of work organization creates economic and organizational conditions for increasing productivity and strengthening labor discipline.
In engineering, there are two main forms of teams: specialized and complex.
Specialized teams are organized from workers of the same profession to perform technologically homogeneous operations (formers, machine operators, etc.). Complex - from workers of different professions using the combination of professions and interconnectedness.
The need to combine professions is determined by technical, social and economic factors. The increase in the share of free machine time in the overall complexity of the operation at the same time increases the complexity and complexity of service jobs, the possibility of sequential or parallel combination of professions. The combination of professions should be considered not only as a means of increasing the intensity of labor and employment of workers, increasing the wages of workers, but also as increasing the content and attractiveness of labor, reducing its monotony, improving culture and professional level. The combination of professions is carried out by mastering workers related or second professions.
A related profession is a profession characterized by a technological or organizational community with the main profession, as well as the performance of the functions of related professions in the workplaces of the main professions. For example, turner-locksmith to repair equipment, machine operator, adjuster, etc.
Organization of multiple service. The essence of multi-machine maintenance is that one worker (team) consistently performs maintenance operations on several units of production equipment, and manual operations on each machine are performed during the automatic operation of other machines.
On the technical side, multi-station service is possible with partial or full automation of machine operation control.
The organization of workplaces for multiple users can be individual and brigade. If the serviced group of machines enters the production line, then their maintenance should be linked to the tact of the production line.
According to the technological homogeneity of the machines, united for multi-station service, there are distinguished: machine doubles, i.e. similar equipment performing the same operations; equipment of the same type on which various operations are performed; technologically different equipment.
The ratio of the duration of the operations included in the multi-station service, there are options: when all operations have equal duration; when their duration is unequal, but multiple; when operations on different machines are not equal and not multiples.
On the organizational side, the condition for multi-maintenance is the following: machine-automatic operation time is equal to the total manual operation time on all other machines:
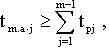
where t м.а · j is the time of machine-automatic operation of this j-th machine, during which the presence of a worker is not required; m is the number of parallel serviced machines; t рj is the total (manual) time of the worker’s employment by servicing the jth machine, including the auxiliary time * , the monitoring time for his work, and the worker’s transition time from one machine to another, i.e.
t рj = t вj + t per j + t nab j .
The time for transition (t lane ) of the worker from the machine to the machine is determined on the basis of 0.015 min. on 1 m path. The active observation time t obs is defined as 5% of t m.a.
If a 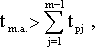 then the worker will have some idle time, but which cannot be considered an idle time.
then the worker will have some idle time, but which cannot be considered an idle time.
If a 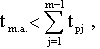 then some machines will stand idle waiting for the worker.
then some machines will stand idle waiting for the worker.
Thus, for effective multimachine maintenance it is necessary to ensure the correct selection of machines, work and the type of multimachine work.
Determination of the multi-machine service rate. Multiple service norm, i.e. the number of machines, in parallel serviced by one worker, is calculated according to
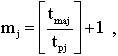
The rounding of service rates is usually downward. In a big way rounding is possible only in the case when the specified amount of the same work is performed on a group of identical machines and when the value of m j is close to the accepted one.
Building a multi-machine maintenance schedule. For a rational selection of works, it is advisable to build multi-station maintenance schedules.
Consider the main stages of construction.
According to the information cards, determine the structure of operational time for each operation included in the multi-station service according to
t op j = t м.а j + t р j
They build a grid of graphics, for which they draw a number of horizontal lines equal to the estimated number of equipment to be combined, leaving gaps between the lines corresponding to the worker’s expectation (approach) or the performance of work not related to a specific machine.
The duration of each element of the labor process in a strict sequence of their implementation is plotted on the schedule grid.
Determine the cycle of multi-station maintenance (t ts .). By t tso is understood the time from the beginning of the service by the workers of the first machine along the route to the time of return and the beginning of a new service by this machine. Almost t ts.o is determined by the j-th machine, which has the greatest operational time of the detail-operation t op j plus the machine idle time for the same operation t pr j , i.e.
T co j = max t op j + t pr j .
Versions of multi-station service schedules are shown in Fig. 8.1.
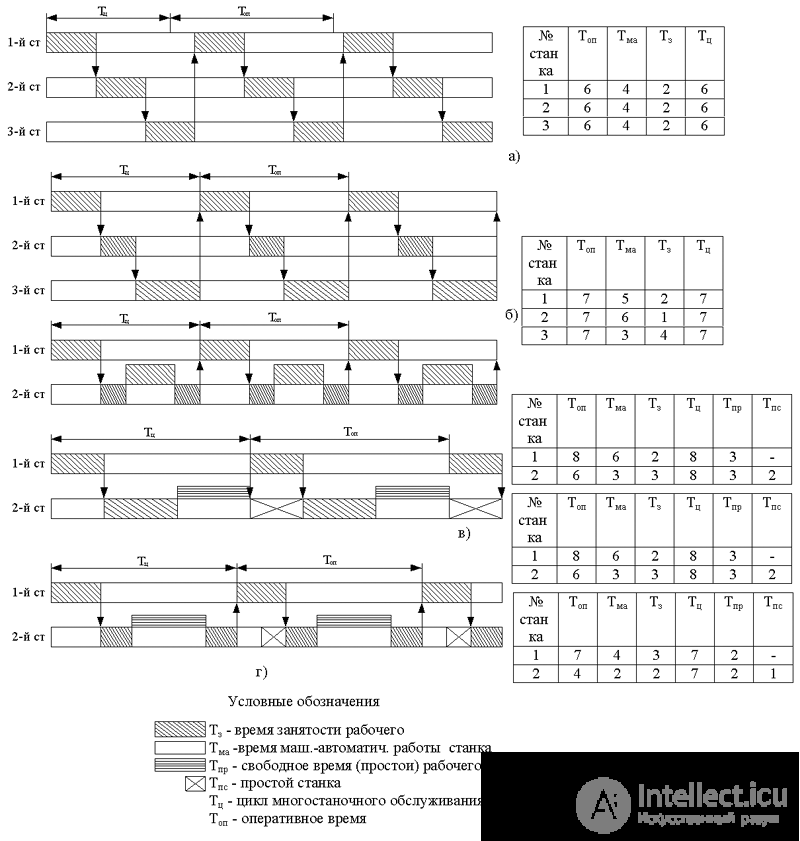
Fig. 8.1 Options for multiple service schedules
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the selected variant of multi-station service occurs in different ways.
a) When working on machine doubles, calculate the coefficients of employment of the worker K s. p and equipment load K s , which are determined by the formulas
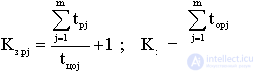
where m j - the number of serviced machines.
b). When working on machines that perform various operations.
In the process of selecting different operations for multi-maintenance, various combinations arise that cause incomplete use of the working time of the worker and the machine. The level of effectiveness of multi-station maintenance options is estimated by the degree of compaction of the working day, characterized by the total employment rate of the worker servicing the machines 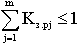 in turn,
in turn, 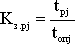
Thus, for the final selection of multi-maintenance options, you need to make sure that the total downtime for serviced machines during a shift does not exceed the allowable (normal) one, and choose the option with the maximum workload.
The calculation of the total coefficients of employment of equipment K s and worker K s. P is made like case a).
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management