Lecture
The basic model of personnel management. The essence and content of the category "personnel management system" are manifested in its functions. In the staffing management of personnel * the unity of two parties - the process and structure - its content is revealed in the process. Hence, the personnel management functions are the functions of the personnel management process. In this case, the functions of the personnel management system is understood as a list of everything that it should do.
At present, in the definition of the functions of the personnel management system, their differentiation and integration, historical inconsistency is preserved. Classifications, lists differ on the number of functions allocated, the degree of their consolidation, etc.
We formulate the original position. The basis for the formation of the target orientation of the personnel management system is a social goal - the achievement of a given degree of satisfaction of the social needs of workers: normal working conditions (compliance with the norms of working conditions, legal protection, provision of social infrastructure, etc.); labor motivation (remuneration, stimulation of creativity, career realization, etc.).
The system of social goals determines the composition of personnel management functions. The initial stage of the formation of functions is the identification of their objects and carriers.
Until recently, the concept of "management" was interpreted as "linear control". This is due to the fact that most of the volume of work on personnel management was taken over by line managers. In the domestic literature there was no presentation of the holistic concept and methodology of the functional division of labor in the field of personnel management.
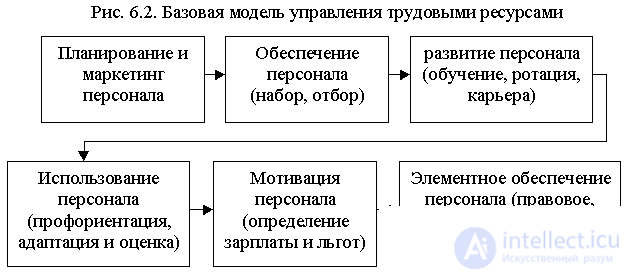
Formulating the general concept and approach to structuring the functional division of labor in the field of personnel management, the following functional blocks are usually distinguished (Fig. 6.2)
T and l and c and 6. 1.
The composition of functional blocks for personnel management
Function block | The content of task functions in the function block |
Staff planning and marketing | Development of personnel policy and strategy of personnel, analysis of personnel potential, analysis of labor markets, planning and forecasting staffing needs, organization of advertising, information support for sources of recruitment |
Staffing | Reception and analysis of marketing information, organization of recruitment, interviews, evaluation, selection and reception of staff |
Staff development | Planning and implementation of business careers and career movements, organization and conduct of training, organization of work with the personnel reserve |
Use of staff | Introduction to the position and adaptation of new employees, the definition of the content and results of labor in the workplace, the assessment of candidates for the vacant position, the current periodic evaluation of personnel, the organization of innovation and inventive activity |
Motivation of the results of work and personnel behavior | Management * of the content and process of motivation of labor behavior, rationing of the labor process, development of wage systems and forms of moral encouragement of staff |
Elemental support of the personnel management process | Legal regulation of labor relations. Accounting and statistics of personnel, information and technical support of the personnel management system |
These functional blocks and determine the structure of the personnel management service.
In each functional block, a certain range of tasks is solved, for example, in the "personnel development" block, tasks of planning and implementing careers, career movements, and organizing and conducting training are solved. In other functional blocks other tasks are solved.
The overall main task of the personnel management service is to ensure the compliance of the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the personnel with the goals of the organization. In this case, the quality characteristics of staff are understood as:
The total number of personnel management personnel, according to foreign data, is 1.0-1.2% of the total number of staff. []
In recent years, there has been an active formation of effective domestic personnel management systems and their gradual inclusion in the general world integration (for example, personnel training in foreign centers, internships, consultations, etc.).
The main directions of staff efficiency improvement. From the standpoint of a systematic approach, any firm is considered as a combination of various structural entities. At the same time, an important feature of the social structure formed in modern conditions is the need to reform it.
In this regard, the creation of management systems, to the greatest extent possible to reveal creative initiative at all hierarchical levels of organizations, has become the main goal of the reorganization of firms.
Thus, first of all, it is necessary to change the psychology of the manager, the style of his economic behavior, the reassessment by managers * of their place and role in the management system. They should create conditions for the development of creative potential, a sense of responsibility both for decision making and for the results of their activities, while feeling their importance.
Understanding that the qualifications of workers and their desire to work well becomes the main productive force and the driving start of production, has led to the reorientation of the strategy * of management of firms to the motivation of labor, gaining great knowledge, skills, labor skills, initiatives, enterprise entrepreneurship.
In many firms, there is a process of reassessment of the place and value of personnel service: their functions, level of competence of employees, technical equipment, methods of work change. To the head of the personnel service there are such requirements as contact, the ability to achieve the intended, competence, creativity, organizational skills, analytical thinking.
With the help of such an understanding of the human factor, an analysis of the activities of personnel, which can be considered economic and sociological, should be carried out. Here, the ways of activating and optimizing human activity, primarily in the production process, are considered, the laws are studied primarily of the economic behavior of an individual.
Rotation of personnel * , its training should be based on the development of a wide range of professions, as well as knowledge, giving him the opportunity to perform many functions, to understand not only production, but also organizational, economic and other aspects of his work.
New managerial thinking implies the need for continuous involvement of workers at all levels, including workers and employees, in management, in the process of identifying problems and making decisions. It follows that a key aspect of effective management is personnel management * .
In most organizations, personnel groups are engaged in two groups: specialists (managers) and practice managers (heads, department heads, vice-presidents). Human resources are a very specific type of resource, and if they are used incorrectly, their effectiveness decreases faster than with other types of resources. Conversely, investing in the resources of this type in any enterprise (except the most capital-intensive) gives a greater effect than in such resources as money, materials and equipment.
Personnel management * is individually oriented. The Japanese School of Management is recognized as one of the most efficient in the world. Its success consists of many components, but the main thing is the ability to work individually with people.
Within the framework of the new managerial thinking, the division and organization of labor is oriented towards a team and brigade approach, i.e. To perform a specific job, a team is selected that acquires the status of a temporary structure. Instead of specialization of the employee on the effective implementation of a specific operation, command structures impose a demand on workers of diverse qualifications. Hence, the training of workers and their training should be based on mastering a wide range of professions. They should understand not only production, but also organizational, managerial, economic or other aspects of their work, master adjacent professions and master the so-called professions of the future.
In modern conditions, a flexible system of material incentives is expected, a combination of uniform wages with the participation of employees in profits (income) received by the company as a whole, which allows reducing the share of wage costs * and the cost of products by 10-40%.
The employee's career is based on how well he performs his duties, working as a member of the team. In this case, the decision to promote an employee is based, as a rule, on three assessments: first, the employee himself and his colleagues; secondly, the immediate supervisor, under whose authority he works; thirdly, higher levels of management representing the interests of the firm as a whole.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management