Lecture
Key performance indicators (English Key Performance Indicators, KPI ) - is indicators of the activities of the unit (enterprise), which helps the organization in achieving strategic and tactical (operational) goals. The use of key performance indicators gives the organization the opportunity to assess their condition and help assess the implementation of the strategy.
 KPIs allow you to monitor the business activity of employees, departments and the company as a whole. The term “key performance indicators (KPI)” is often used in the Russian translation of “key performance indicators” (KPI), but this is not quite true [1] .
KPIs allow you to monitor the business activity of employees, departments and the company as a whole. The term “key performance indicators (KPI)” is often used in the Russian translation of “key performance indicators” (KPI), but this is not quite true [1] .
With the translation within the meaning of the words key (a key characterizing the degree of achievement of any goal, essential for one of the company's activities) and indicator (indicator, indicator), problems do not arise, but the word performance cannot be unequivocally interpreted, although technically it is “performance , Efficiency. Correct wording can be found in ISO 9000: 2008. He divides the word performance into two terms: performance and efficiency. According to the standard, performance is the degree of achievement of the planned results (the company's ability to focus on results), and efficiency is the ratio between the results achieved and the resources expended (the company's ability to realize its goals and plans with a given quality level expressed by certain requirements - time, cost, degree of achievement of the goal). The word performance combines performance and efficiency. Thus, the correct translation of the term KPI will be a “key indicator of the result of an activity,” since the result of an activity contains both the degree of achievement and the cost of obtaining a result [1] .
KPI is a tool for measuring goals. If the indicator that you came up with is not related to the goal, that is, it is not formed on the basis of its content, then this KPI cannot be used. Technologies of setting, revising and controlling goals and objectives formed the basis of the concept, which became the basis of modern management and is called “Management by Objectives”.
Management by Objectives is a method of management activity that includes:
The founder of the "Management by Objectives" is Peter Drucker (it. Peter Ferdinand Drucker (1909-2005)). It was he who turned the management - an unpopular and not respected specialty in the 50s of the XX century into a scientific discipline. Peter Drucker is also the founder of the performance measurement system - goals through key performance indicators. According to Drucker, chiefs should avoid “time traps” when they are involved in the process of solving current day-to-day tasks, because this leads to the fact that they begin to forget to perform tasks aimed at achieving results (goals). The modern embodiment of management by objectives is the “KPI System”, which includes many management concepts that have emerged over the past 20–30 years and complement the classic “Management by objectives”.
According to Peter Drucker, only a few areas of management have such a great influence on the organization as the evaluation of the activities of the divisions and the company as a whole. However, the assessment, emphasizes Drucker, today one of the most poorly developed areas of management. So as a result of a survey conducted in the United States, it became clear that 60% of top-level managers are dissatisfied with their performance measurement systems. According to Russian estimates, the number of Russian managers is even higher, more than 80%. This dissatisfaction is expressed in the absence of a connection between plans, execution, results and motivation [2] .
KPI and staff motivation have become inseparable concepts, as using these indicators (KPI) you can create a perfect and effective system of motivation and incentives for company employees.
Depending on the company's strategy, there are different KPIs. Basically they are used to determine the performance of administrative and management personnel. For example, in the strategic goal “to increase the average income per client from 10 rubles to 15 rubles for 2008”, the key indicator of effectiveness is “average income per client”. KPI is not Key to success. In the example above, the key success factors will be anything that is needed to achieve this goal, for example, organizing the production of a new product.
Key performance indicators can be divided into:
The lagging include financial performance. Financial indicators show a connection with the wishes of the owner and the company's ability to generate cash flows, but because of their late nature they cannot describe the current efficiency of the divisions and the company as a whole [3] .
Operational (leading) indicators tell about the current activities of the divisions and the company as a whole, simultaneously and indirectly answering questions about what cash flows can be in the future, as well as the quality of processes and products, the degree of customer satisfaction [3] .
Key performance indicators are part of the Balanced Scorecard system, which establishes a causal relationship between goals and indicators in order to see patterns and mutual factors of influence in business - the dependence of some indicators (performance) on others.
Development of KPI is recommended to be carried out in a number of stages [4] :
1. Pre-design work:
2. Development of the KPI system methodology:
3. Development of KPI information system:
4. Completion of the project. Putting the KPI system (methodology and information system) into industrial operation.
When developing a KPI methodology, it is important to focus on:
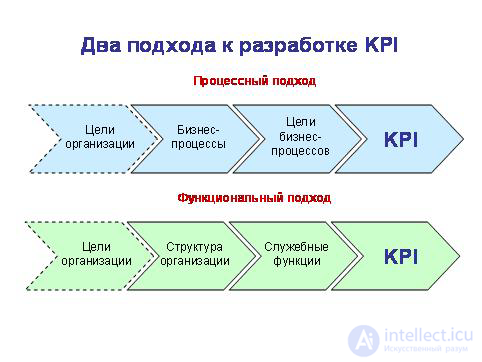
In practice, the development of KPI uses process and functional methods. Based on the strategy and objectives of the organization, the first involves the description and optimization of the business processes of the organization, the second - the formation of an organizational structure that reflects the main activities and the composition of business units. The features of these approaches are analyzed by Oleg Kulagin .
As part of the management method for the objectives and the development of key performance indicators (KPI), we consider two practical approaches to the development of KPIs for an organization, divisions and employees - process and functional.
In the continuation of the series of articles devoted to the management method for the objectives and the development of key performance indicators (KPI), we consider two practical approaches to the development of the organization's KPIs, divisions and employees - process and functional.
The first approach is process . In accordance with it, the description and optimization of the organization’s business processes takes place on the basis of the strategy and objectives. The result of this work should be not only the description in one or another model (notation) of business processes "as is" and "as it should", but also the formulation of the objectives of each business process. At the same time, the goals of the processes are formulated in general terms as goals-intentions without reference to certain indicators, terms and standards. For example, if in the company and, in particular, in the sales department, the “Search for new customers” business process is formalized, then its immediate goals are “Expanding the customer base” and “Growth in the number of new customers”. For the business process "Management of accounts receivable" the goal can be formulated as "Reduction of overdue receivables" or "Increase in receivables turnover". For the business process “Stock management of products in stock,” the goal is formulated as “Increasing inventory turnover”. The business process “Fulfillment of customer orders” may have several objectives: “Compliance with the delivery time of goods”, “Minimization of logistic defects”, “Meeting customer requirements for quality and completeness of orders”. And so for any process occurring in the organization and its divisions. The process of any level corresponds to one or several goals, which are formulated and fixed in the established documentation and regulations of the company's business processes.
If we know the goals of business processes, then we select the appropriate indicators for them, with the help of which we can assess the degree of achievement of these goals. Examples of business processes, business process goals and business process KPIs are shown below.
|
Business processes |
Goals of business processes |
KPI business processes |
|
Looking for new clients |
|
|
|
Receivables Management |
|
|
|
Stock management |
|
|
|
Fulfillment of customer orders |
|
|
|
... |
... |
... |
Business process performance indicators are KPIs of managers and employees who are responsible for the results of these business processes. We can move from business processes to official positions in an organization using matrices of responsibility for business processes and divisions. Thus, each employee - from the general director to ordinary employees - receives his own set of KPIs, with the help of which goals-results are formulated and their work is evaluated for a certain period of time (month, quarter, year).
All right, all great. But there is one small difficulty. For the practical implementation of the process approach to the development of KPI, a description and formalization of the organization’s business processes should be performed. According to the most optimistic estimates, currently only about 5% of Russian enterprises have a description of their business processes. What to do the rest? Follow their example and go to process management together? But overnight will not work. This is a titanic work, which is far from always a success. But even in case of its successful completion, there is no guarantee that the enterprise will gladly accept this description as a guide to action and will live under a new charter. But even if this happened, and the business processes “as it should be” earned, then over time the description of these business processes often begins to lag behind real life. The work of the company gradually accumulates changes that are not adequately reflected in the schemes and regulations of business processes. As a result, the description of the processes becomes outdated and begins not to help, but to hinder and slow down the real processes occurring in the organization. At best, the old description of dead weight lies in the office of the director or in the quality management department and does not affect the efficiency of work in any way. The process description should be proactive , i.e. continuously updated at the pace of real change and even a little bit faster. This is the right way, but too troublesome, difficult and thorny. And while not all organizations are ready to embark on it and follow this path. What to do? Abandon KPI as an overseas curiosity, which we are not yet "in the teeth"? Is it possible to develop a system of key performance indicators without a description of business processes? Can. Using a functional approach.
So, the second approach is functional . In accordance with it, on the basis of the strategy and objectives of the enterprise, its organizational structure is formed, reflecting the main activities and the composition of business units (divisional structure) and the functions or projects performed in each of these areas (linear-functional, matrix, project structure). Any organizational structure determines the composition of positions (staffing) and the relationship of responsibility between them. Then, for each position in the structure of the organization, its service functions are determined according to the product method. How this is done, we have already discussed in the previous article “Service functions as the basis of KPI”. If we know the service functions of managers and employees, then for each of them we develop certain indicators to assess the degree of fulfillment of this function.
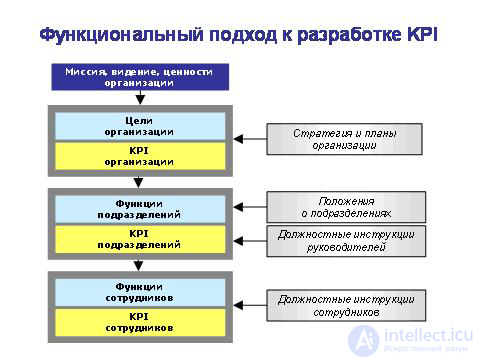
In accordance with this approach, performance indicators at different levels (organization-division-employee) are developed based on the goals of the enterprise and the service functions of managers and employees of the divisions. At the organization level, for each goal, we select or develop appropriate KPIs to assess the degree of achievement of this goal. Similarly, at the level of departments and employees for each function, we select one or more indicators that directly or indirectly assess the level of performance of this function. Поскольку функции подразделений получены в результате декомпозиции целей предприятия, а функции сотрудников логически вытекают из функций подразделений, то KPI сотрудников будут обеспечивать KPI подразделений, а KPI подразделений, в свою очередь, будут «работать» на KPI организации. Показатели разных уровней взаимосвязаны как причина и следствие. Так цели организации последовательно передаются «сверху вниз» на уровень подразделений и сотрудников.
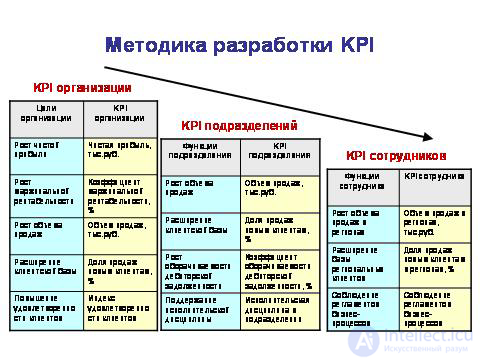
Consider a few examples.
Пример 1. Переход от целей к KPI организации.
|
Цели |
Показатели эффективности |
|
Финансовые цели |
|
|
1. Увеличение прибыли предприятия. |
·Чистая прибыль, тыс. руб. ·Маржинальная прибыль, тыс. руб. |
|
2. Повышение рентабельности и ликвидности предприятия.
|
· Коэффициент рентабельности продаж. · Коэффициент рентабельности активов. · Коэффициент рентабельности оборотных активов. · Коэффициент рентабельности внеоборотных активов. · Коэффициент рентабельности собственного капитала. ·Коэффициент маржинальной рентабельности. · Коэффициент текущей ликвидности. · Коэффициент быстрой ликвидности. · Чистый рабочий капитал .
|
|
3. Рост оборачиваемости ресурсов предприятия.
|
· Коэффициент оборачиваемости дебиторской задолженности. · Коэффициент оборачиваемости запасов. · Коэффициент оборачиваемости кредиторской задолженности. · Коэффициент оборачиваемости активов . |
|
Рыночные цели |
|
|
4. Увеличение объема продаж предприятия.
|
· Sales (revenue from sales), thousand rubles · Cash flow, thousand rubles
|
|
5. Growth in the share of imported and own brands in the company's turnover.
|
· Volume (share) of sales of imported and own brands, ths. Rub. (%) · Volume (share) of sales of art products, thousand rubles (%) · Volume (share) of sales of related products, thousand rubles (%)
|
|
6. Expansion and preservation of customer base.
|
· Volume (share) of sales to new customers, RUB thousand (%) · Volume (share) of sales to regular customers, thousand rubles (%) · Size of customer base. · Size of regional network.
|
|
7. Expansion of direct distribution in cities of Russia numbering over 100,000 people (art channel, retail book and stationery networks).
|
· Volume (share) of sales to retail customers in Russia, ths. Rub. (%)
|
|
8. Expansion of indirect distribution in the regional cities of Russia (stationery channel).
|
· Volume (share) of sales in the stationery channel in Russia, ths. Rub. (%)
|
|
9. Expansion of the distribution of goods under its own brands in the CIS countries, the Baltic States and far abroad.
|
· Volume (share) of sales of goods under their own brands in the CIS countries, the Baltic States and other countries, thousand rubles. (%)
|
|
10. Expansion of the distribution of school stationery and related products in the CIS and Baltic countries.
|
· Volume (share) of sales of school stationery and related products in the CIS and Baltic countries, ths. Rub. (%)
|
|
11. Development of new distribution channels.
|
· Volume (share) of sales in new distribution channels, ths. Rub. (%)
|
|
12. Increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
|
· Customer satisfaction index.
|
|
13. Achieving the company's competitive advantages in quality, range, service and availability of goods for customers.
|
· Customer satisfaction index.
|
|
14. Forming and maintaining a sustainable base of alternative suppliers.
|
· The share of individual suppliers in the volume of the company's purchases,%. · Volume (share) of purchases from regular suppliers, thousand rubles (%) · Supplier satisfaction index.
|
|
15. Creating a competitive advantage of the company in the labor market and the market of suppliers.
|
· Staff satisfaction index. · The turnover rate. · Supplier satisfaction index.
|
|
Goals for internal processes |
|
|
16. Increase organization productivity.
|
· Net profit per employee, thousand rubles
|
|
17. Ensuring the required quality and lead time.
|
· Customer satisfaction index. · Satisfaction of applications of buyers for the goods of group A,%. · The number of claims from customers.
|
|
18. Reducing costs that do not add value to the company and customers.
|
· Compliance with the organization's budget,%.
|
|
19. Increased staff satisfaction.
|
· Staff satisfaction index.
|
|
20. Improvement and formalization of business processes of the organization.
|
· Satisfaction with internal customers. · The quality and timeliness of providing materials, information, documents. · The quality of business process regulations. · The level of formalization of business processes,% (the number of regulations of business processes relative to the total number of business processes of the organization).
|
|
Learning and Development Goals |
|
|
21. Modernization of storage technology.
|
· Compliance with the project schedule. · The quality of the project (stages, activities).
|
|
22. Development and implementation of electronic document management system.
|
· Compliance with the project schedule. · The quality of the project (stages, activities).
|
|
23. Development and implementation of an automated customer order processing system.
|
· Compliance with the project schedule. · The quality of the project (stages, activities).
|
|
24. Development and implementation of an automated procurement planning system.
|
· Compliance with the project schedule. · The quality of the project (stages, activities).
|
|
25. Improving the management accounting system.
|
· Compliance with the project schedule. · The quality of the project (stages, activities).
|
|
26. Development and implementation of a system of evaluation and remuneration of staff on key performance indicators.
|
· Compliance with the project schedule. · The quality of the project (stages, activities).
|
|
27. Improving the system of non-material incentives.
|
· Compliance with the project schedule. · The quality of the project (stages, activities).
|
|
28. Formation of the management team.
|
· Compliance with the project schedule. · The quality of the project (stages, activities).
|
|
29. Development of core competencies and staff development.
|
· Assessments of staff competencies and qualifications. · Number of employees trained.
|
|
30. The development of organizational culture aimed at meeting customer needs, achieving results, innovation and teamwork in work.
|
· Evaluation of staff competencies. · Staff satisfaction index.
|
Example 2. Transition from service functions to employee KPI (for the head of sales department).
|
Service functions |
Key performance indicators |
|
Increase customer satisfaction.
|
Customer satisfaction index.
|
|
Satisfying customers' requirements and creating a firm's competitive advantages in terms of quality and lead times.
|
· Customer satisfaction index. · Average lead time, hour. · The number of claims (complaints) buyers.
|
|
Increase margin profitability of the enterprise.
|
· Margin profitability ratio,%. · The coefficient of specific marginal profitability,%. |
|
Increase sales profitability. |
Return on sales ratio,%. |
|
Compliance with the receivables turnover ratio.
|
· The turnover Ratio of receivables,%. · Overdue receivables, thousand rubles · The share of overdue receivables,%. |
|
Increase overall unit sales.
|
· Sales volume, thousand rubles · Cash flow, thousand rubles |
|
Growth in sales to regional buyers.
|
· Sales to regional customers, thousand rubles · Share of sales to regional customers,%. |
|
Increase in the share of sales to retail networks.
|
· Sales to retail chains, thousand rubles · Share of sales to retail networks,%. |
|
Expansion and preservation of customer base.
|
· Size of customer base (number of customers). · Number of loyal customers. · The share of loyal customers. · Sales to new customers, thousand rubles. · Share of sales to new customers,%. · Sales to regular customers, thousand rubles · Share of sales to regular customers,%. |
|
Development of competencies and staff development.
|
Employee competency scores, points. |
|
Increase satisfaction and loyalty of the department staff.
|
· Staff satisfaction index. · Staff loyalty index. |
|
· Compliance and improvement of the business process regulations of the department. · Development and improvement of job descriptions of employees. · Introduce a system of assessment and remuneration in the division according to key performance indicators. · The formation and development of an organizational culture focused on the needs of the client, the achievement of results, mutual commitment in relations and teamwork in work. |
Internal customer satisfaction index. |
|
Compliance budget unit. |
Deviation from the budget unit, thousand rubles.
|
|
Compliance with the rules of operation of technical systems and equipment. |
Compliance with the rules of operation of technical systems and equipment. |
|
· Timely and clear statement of tasks. · An objective assessment of the results of work. · Motivating management style, favorable psychological climate in the unit. ·Создание условий, обеспечивающих эффективную работу сотрудников подразделения (физические условия труда, оснащенность рабочих мест, расходные материалы). ·Психологическая и профессиональная поддержка в трудных ситуациях. |
Индекс удовлетворенности внутренних клиентов. |
|
Соблюдение необходимого качества и сроков предоставления информации и документов (в соответствии с регламентом документооборота организации). |
·Индекс удовлетворенности внутренних клиентов. ·Соблюдение регламента документооборота. |
Пример 3. Переход от служебных функций к KPI сотрудника (для начальника отдела закупок).
|
Служебные функции |
Ключевые показатели эффективности |
|
Увеличение маржинальной рентабельности предприятия.
|
·Коэффициент маржинальной рентабельности, %. ·Коэффициент удельной маржинальной рентабельности, %. |
|
Рост объема продаж предприятия.
|
Объем продаж, тыс.руб. |
|
Compliance with the standards of accounts payable turnover.
|
Payables turnover ratio,%.
|
|
Increased inventory turnover.
|
Inventory turnover ratio,%
|
|
Forming and maintaining a sustainable base of alternative suppliers that meet the requirements of the enterprise (supplier reliability, compliance with contractual obligations, quality of goods, range, service, etc.).
|
The quality and stability of the supplier base.
|
|
Increasing the proportion of purchases from suppliers and manufacturers.
|
The share of purchases from manufacturers,%.
|
|
Development of competencies and staff development.
|
Employee competency scores, points. |
|
Compliance with the required delivery times.
|
The share of applications for additional purchases completed on time,%. |
|
Permanent availability of goods in stock.
|
· Share of orders completed without additional purchases,%. ·Среднее время выполнения заказа, час. ·Индекс удовлетворенности покупателей. |
|
Достижение конкурентного соотношения «качество/цена» на закупаемые товары. |
Индекс удовлетворенности покупателей. |
|
Повышение удовлетворенности и лояльности сотрудников отдела.
|
·Индекс удовлетворенности персонала. ·Индекс лояльности персонала. |
|
·Соблюдение и совершенствование регламентов бизнес-процессов подразделения. ·Разработка и совершенствование должностных инструкций сотрудников. ·Внедрение системы оценки и оплаты труда в подразделении по ключевым показателям эффективности. ·Формирование и развитие организационной культуры, ориентированной на потребности клиента, достижение результата, взаимную обязательность в отношениях и командность в работе. |
Индекс удовлетворенности внутренних клиентов. |
|
Соблюдение бюджета подразделения. |
Отклонение от бюджета подразделения, тыс.руб.
|
|
Compliance with the rules of operation of technical systems and equipment. |
Compliance with the rules of operation of technical systems and equipment. |
|
· Timely and clear statement of tasks. · An objective assessment of the results of work. · Motivating management style, favorable psychological climate in the unit. · Creation of conditions ensuring effective work of the division employees (physical working conditions, equipment of workplaces, consumables). · Psychological and professional support in difficult situations. |
Internal customer satisfaction index. |
|
Compliance with the required quality and timing of information and documents (in accordance with the organization’s document management regulations). |
· Internal customer satisfaction index. · Compliance with the rules of document flow. |
Thus, we get a set of indicators of the organization, units and employees. The composition of the indicators should be balanced. Therefore, it is convenient and desirable to immediately group them into four types: team - individual, quantitative - qualitative. By filling in the following table for each post, we get a KPI library of posts.
KPI posts.
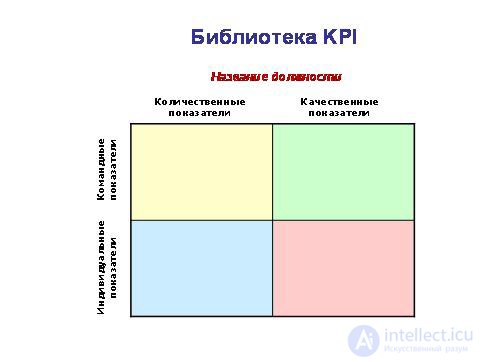
Example 4. Library KPI head of the department of wholesale sales (trading house).
|
Team quantitative indicators
· Sales volume, thousand rubles
· Sales to regional customers, thousand rubles
· Share of sales to regional customers,%.
· Sales to retail chains, thousand rubles
· Share of sales to retail networks,%. Margin profitability ratio,%.
· The coefficient of specific marginal profitability,%.
· Average lead time, hour.
· The number of claims (complaints) buyers.
· Size of customer base (number of customers).
· Number of loyal customers.
· The share of loyal customers.
|
Team quality indicators
· Customer satisfaction index.
· Staff satisfaction index.
· Staff loyalty index.
|
|
Individual quantitative indicators
· Return on sales ratio,%.
· The turnover Ratio of receivables,%.
· Overdue receivables, thousand rubles
· The share of overdue receivables,%.
· Cash flow, thousand rubles
· Объем продаж новым клиентам, тыс.руб.
· Доля продаж новым клиентам, %.
· Объем продаж постоянным клиентам, тыс.руб.
· Доля продаж постоянным клиентам, %.
· Отклонение от бюджета подразделения, тыс.руб.
|
Индивидуальные качественные показатели
· Оценки компетенций сотрудников, баллы.
· Индекс удовлетворенности внутренних клиентов.
· Соблюдение правил эксплуатации технических систем и оборудования.
· Соблюдение регламента документооборота.
|
Пример 5. Библиотека KPI начальника отдела закупок (торговый дом).
|
Командные количественные показатели
· Коэффициент маржинальной рентабельности, %.
· Коэффициент удельной маржинальной рентабельности, %.
· Объем продаж, тыс.руб.
· Среднее время выполнения заказа, час.
|
Командные качественные показатели
· Индекс удовлетворенности покупателей.
· Индекс удовлетворенности персонала.
· Индекс лояльности персонала.
|
|
Индивидуальные количественные показатели
· Коэффициент оборачиваемости кредиторской задолженности, %.
· Коэффициент оборачиваемости запасов, %.
· Доля закупок у производителей, %.
· Доля заявок на дополнительную закупку, выполненных в срок, %.
· Доля заказов, выполненных без дополнительных закупок, %.
· Отклонение от бюджета подразделения, тыс.руб.
|
Индивидуальные качественные показатели
· Оценки компетенций сотрудников, баллы.
· Качество и стабильность базы поставщиков.
· Индекс удовлетворенности внутренних клиентов.
· Соблюдение правил эксплуатации технических систем и оборудования.
· Соблюдение регламента документооборота.
|
Таким образом, спускаясь от целей предприятия и функций подразделений и сотрудников к разработке KPI, позволяющих оценивать их исполнение, мы получаем для каждой должности библиотеку показателей, которые могут использоваться для оценивания результатов работы сотрудников. В состав библиотеки KPI должности могут входить разнообразные показатели, но для проведения оценки сотрудника за определенный период времени (месяц, квартал) мы выбираем из библиотеки самые важные KPI, чтобы сконцентрировать внимание и энергию сотрудников на достижении наиболее приоритетных результатов. Как это делается? Об этом поговорим в следующей статье.
KPI, позволяющих оценивать их исполнение, мы получаем для каждой должности библиотеку показателей, которые могут использоваться для оценивания результатов работы сотрудников. В состав библиотеки KPI должности могут входить разнообразные показатели, но для проведения оценки сотрудника за определенный период времени (месяц, квартал) мы выбираем из библиотеки самые важные KPI, чтобы сконцентрировать внимание и энергию сотрудников на достижении наиболее приоритетных результатов.
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management