Lecture
Developing an organization’s strategy is not an end in itself strategic planning * . This work makes sense if the strategy is successfully implemented in the future. The result of the functioning of the strategic planning system is a set of planning documents that reflect the adopted strategic decisions and resource allocations. The basic premise underlying the structurization of a system of plans reflects the conclusion of management theory — the law of the necessary diversity * , according to which a complex system requires a complex control mechanism.
A modern organization should develop mainly four groups of interrelated plans (Fig. 5.4).
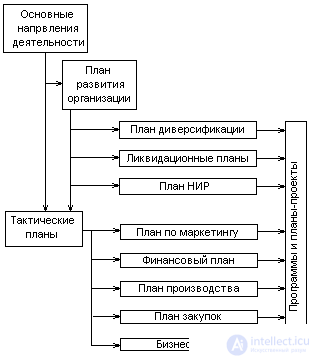
Fig. 5.4. System of organization development plans
The main activities are a strategy for the foreseeable future - 10 - 15 years.
The development plans of the organization for a period of 1 to 5 years are the prospects for improving production, the transition to a new generation of products, a new technology.
Tactical plans - they regulate the current activities of the organization.
Programs and plans - projects that are targeted: the development of new products and technologies, reducing production costs, saving energy, penetrating new markets, etc.
The main activities . This plan is also called strategic. It serves as the pinnacle of the system of plans because it characterizes the main purposes of the organization, its goals and strategies. It serves as a guideline for all other plans.
Organization development plan . It establishes the activities that are necessary to create new generations of products and services, outlines ways to reach new positions defined in the main activity.
The development plan serves as a guideline for the development of a diversification plan, which is characterized by the creation of new types of products, services, markets, designed to supplement or replace the products produced; a liquidation plan that shows which elements the organization should free itself from (from products, services, property or structural units); R & D plan, which reflects the development of new products and technological processes, taking into account significant demand or new markets for goods and services already produced. The R & D plan affects all elements of the organization — products, markets, finance, and management.
Tactical plans . These plans are called current activity plans or profit plans. They are focused on those activities through which manufactured goods and services are produced and supplied to existing markets. Plans for current activities are supported by plans for each functional area: sales, finance, production, procurement, etc. These plans are closely linked to the strategic plan, although they are not part of it.
Tactical plans serve as the main instrument for the implementation of strategic plans and, from this point of view, have some differences from the latter, which must be taken into account in practical work:
It is also important to emphasize here that in the conditions of transition to a market economy, the structure of tactical plans, the principles of their development and the priorities of the main sections change significantly. Thus, the organization’s annual plan typically includes four main sections: a marketing plan; a financial plan; production plan and procurement plan . The product marketing plan, which is developed through a marketing approach, is the guide for all subsequent sections. Depending on the stage of development of market relations and the prevailing external conditions of the company's activities, the priorities of the sections of the plan and their significance change. On the first place there can be a sales plan, or a financial plan, or a production one.
Each strategic plan is necessarily supported by a set of programs and project plans. For example, an organization’s development plan is justified by short, medium and long-term programs specifying the activities included in it. These may be programs for developing and introducing a new type of product; development and implementation of a new management information system; restructuring of the organizational structure of the company and others. Programs, in turn, are supported by specific projects. Each project is unique in the sense that it has a certain cost, implementation schedule and technical and economic parameters.
Let us note an important methodological feature of the formation of a system of planning documents in strategic planning — the need for a mechanism to adapt an organization’s plans to changing external development conditions. The adaptive nature of the plans suggests that they must be sufficiently flexible, easily adaptable to unexpected changes in external factors. Consequently, in order to ensure the adaptive nature of strategic planning, all types of plans, especially tactical ones, must provide for contingency measures. These actions should be implemented through a well-known methodical technique - situational planning .
The system of plans, programs and projects in addition to performing the main management function is also a necessary tool for the distribution of strategic and tactical resources . In fact, a preliminary indicator of a plan or program is the desire of management to allocate resources for their implementation. Plans help to allocate resources in areas that, in the opinion of management, are the most effective and lead to the achievement of goals. However, the plans do not give a complete answer to the questions, what specific resources and in what quantities are required.
There are several methods for identifying needs and allocating resources necessary for implementing an organization-selected strategy and coordinating follow-up actions. At the first planning stage, expert evaluations, various integrated methods, based on standards, budgets are used. But the most common formal planning method used to ensure consistency between different plans and the allocation of resources is the development of budgets.
Development of the budget is a rather complicated and responsible work, which is carried out within the framework of strategic planning. It begins with the announcement by the leadership of the organization of the overall mission of the company and the goals of the CPS and individual units. Then CPS and units begin to develop preliminary estimates or budgets for a certain planning period. These documents are presented to the management, which carefully examines them, and the plans of the CXP make the necessary adjustments and guidelines to clarify budgets. In fact, at this stage, the distribution of available resources among CXPs takes place, and the funds from which they will be financed or supplied are determined. At the final stage of budget development, on the basis of guidance from the management, detailed item-by-item accounting of resources and sources of their receipt occurs.
As a rule, the process of resource allocation between CPS, divisions, plans and programs does not end with the development of the final budget. The adaptive nature of strategic plans suggests periodic adjustment of budgets in accordance with changes in the goals or strategies of the organization or its units. Therefore, it is very important to create a permanent mechanism for the redistribution of resources. This problem can be solved by the methods already mentioned. A convenient tool for carrying out this work is the well-known method of reallocating resources using a network graph. Along with a good and visual structuring of the complex of work performed, their interconnection and interdependence, it is possible to use for the redistribution of resources of modern computing equipment.
Strategy planning is a type of management activity that requires considerable time and effort. Since the functions of strategic planning are carried out by people, then, as noted above, this process must be formalized and must be managed. Management * of the implementation of the strategy should also be carried out through the stimulation of the attitude of managers and workers at all levels that should be due to them. Especially here it is necessary to note the need to create and constantly maintain a good organizational and psychological climate, instill in employees the idea that permanent changes are a natural state of the organization’s development, and these changes need to be constantly ready.
The main condition for the effective functioning of the strategic planning system is the constant attention to it from the top managers, the ability to prove to them the need for planning, to involve a wide circle of employees in developing and implementing the strategy. Such attention is especially important at the first stage of implementation of the planning system in the organization. After the implementation of strategic planning and its distribution across all divisions, after it confirms its effectiveness and the number of employees who realize its need increases, the management process can be structured in many ways, and it will play a significant role in rewarding employees for valuable suggestions for improvement. manufactured products, the development of new markets, a planning system, the development of a new strategy * .
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management