Lecture
Purpose and types of scientific research. Scientific preparation of production (GMP) * is the first stage of the SONT system.
NPP is a set of interrelated processes of scientific search and substantiation of possible directions for the development and creation of new equipment, technology and organization of production, ensuring an increase in efficiency both in the field of production and in operation.
The criteria for achieving the main goal of the NPP are the minimum resource expenditures (financial, human, time) and the maximum use of the achievements of the scientific and technical process.
The basis of the NPP is scientific research (NI). Their characteristic features are:
By the nature of the final result, NI are divided into:
Basic research - form the basis of the scientific potential of knowledge about the object under study, expand and deepen the level of representation.
They are either purely theoretical, or rely on the most complex and very accurate experiments.
Search studies. They are focused and carried out when the available scientific and technical knowledge and solutions are not enough to carry out the necessary developments. Their main goals are:
Applied research. They are reduced to the solution of specific problems of creating products and materials with certain properties, objects of new technology or new technological processes.
They can either be the initial stage of development, or be carried out in parallel with it (improvement of schemes, work processes, increase of reliability, etc.). Include a significant amount of experiments, analysis, the choice of a rational solution.
Development - a transitional stage from research to technical preparation of production.
Development can be research and development (R & D) and pilot industrial (ODA).
ODA provide for bringing the results to the conditions of industrial development and include in the necessary volume the implementation of design and working documentation, experimental verification and revision of the object in accordance with the requirements of production and operation.
The effectiveness of the fundamental and most of the search NI is evaluated using scientific and technical indicators:
The effectiveness of applied (CIR, R & D, ODA) NI is evaluated using:
The effectiveness of indicators of social significance (improvement of working conditions, increasing automation of processes, changing the professional composition and level of performers, etc.).
The functional block of the tasks of the subsystem NPP. NPP at the stages of its implementation includes a number of stages and their functional tasks. Each type of NO is characterized by a specific sequence of works and their content.
Search studies include:
Applied research * . They are carried out similarly to search, accompanied by a significant number of experiments and tests.
Research and development (R & D) include the steps of:
Organizational structure * of the SPE subsystem. The tasks of the SPE subsystem implement research organizations distinguished by the nature and scope of work performed:
Each of the specified number of organizations has its own specificity and organizational and legal form (AOOT, AOZT, government agency, etc.).
The organizational structure of a research institute (SRI) is understood as the composition of its main and auxiliary departments, sectors and laboratories, model and experimental workshops, services and administrative and management units, the form of their specialization and the system of production relations.
The structure of a scientific research institute can have four and five-step scheme of functional and organizational construction (fig. 7.2.)
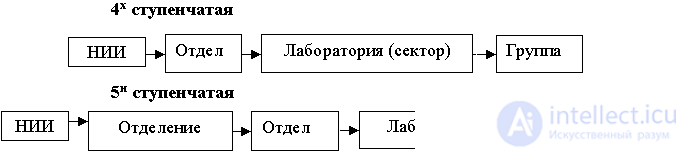
Fig. 7.2. Organizational structure of research institutes.
The main structural subdivision of the scientific research institute is the research department (NIO).
The structure of an NIO can be built according to one of the principles:
The thematic structure provides for the formation of groups of scientists and engineers of various specialties to solve the target scientific problem. Works are performed sequentially in a closed loop. (For example: the creation of laser systems. Development participants: physicists, chemists, electronic engineers).
The branch principle provides for the unification of employees of one specialty in one unit. Various thematic work is carried out in parallel with extensive cooperation between individual departments.
The mixed principle provides for the creation in one unit and thematic and specialized groups.
Each organizational structure * has its own advantages and disadvantages, which should be taken into account when planning work.
The elemental composition of the subsystem SPE. To perform the above functions, the SPE subsystem has the following elemental composition:
Comments
To leave a comment
Management
Terms: Management