Along with the noise figure, the concept of noise temperature is widely used, which characterizes the self-noise of the quadrupole, recalculated to its input. This value is the thermal equivalent of the intrinsic noise of the quadrupole and shows how many degrees the source should be heated so that the output noise caused by it equals the intrinsic noise.
By analogy with (*), we write
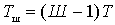 ,(four)
,(four)
where T is the absolute temperature of the source.
Thus, the noise temperature characterizes the absolute level of the self-noise of the quadrupole recalculated to the input, with which the source is matched.
It should be emphasized that the effective noise temperature of the device does not depend on the noise temperature of the source. Comparing 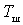 with
with 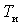 An important conclusion can be made about the relationship between the intrinsic noise level of the device and the noise level of the source. If, for example, it turned out that
An important conclusion can be made about the relationship between the intrinsic noise level of the device and the noise level of the source. If, for example, it turned out that 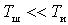 , it is obvious that there is no point in reducing the device's own noises. The concept of effective noise temperature is especially convenient when studying low-noise amplifiers whose noise figure is close to 1. For example, when W = 1.1, we have
, it is obvious that there is no point in reducing the device's own noises. The concept of effective noise temperature is especially convenient when studying low-noise amplifiers whose noise figure is close to 1. For example, when W = 1.1, we have 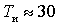 K. Substituting (4) into (3) we get
K. Substituting (4) into (3) we get
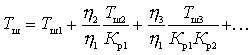 .
.


Comments
To leave a comment
Devices for the reception and processing of radio signals, Transmission, reception and processing of signals
Terms: Devices for the reception and processing of radio signals, Transmission, reception and processing of signals