Lecture
Communication systems should be designed in such a way that they can efficiently, that is, timely and losslessly transmit the information contained in the original message. Consider the main characteristics of the most common types of messages: sound and optical.
Sound is the quantitative movement of particles of an elastic medium, propagating in the form of waves in gaseous, liquid or solid media and perceived by the human senses.Sources of sound can be any phenomenon that causes local pressure changes. Oscillating solids are widely used as sound sources, for example, strings and decks of musical instruments, speaker cones, phone membranes and various electroacoustic transducers. Microphones and other acoustoelectric transducers are used as sound receivers.
A significant proportion of audio messages are speech signals. Speech sounds are formed as a result of the passage of air flow from the lungs through the vocal cords and the mouth and nose. The frequency of the colo *** of the main tone lies in the range from 50 ... 80 Hz (bass) to 200 ... 250 Hz (children's and female voices). In addition to the fundamental tone, human speech contains a large number of harmonics (up to 49), and their amplitudes decrease with increasing frequency.
The energy spectrum of a speech signal is the averaged energy distribution of sound coils in a frequency band. The degree of influence of sound on the senses is usually estimated in relative units, calculated as the level of sound pressure:β = 10 lg [П² (f) / П² 0 ] , [dB], (4.13)
where P2 (f) is the average square of the sound pressure exerted by the harmonic components of the sound, located in the vicinity of the frequency f in the frequency band equal to 1 Hz; P 0 - the threshold of hearing (minimum sound pressure, which begins to be felt by a person with normal hearing at a frequency of 600 ... 800 Hz).Hereafter, the decimal logarithm of the ratio of two quantities of the same dimension is used as the quantitative characteristics of signals and communication systems. One unit of this size is called Bel (denoted by [B]) in honor of the American scientist Alexander Bell. The unit of measurement is one Bel - this is a fairly large value, and in practice the unit of measurement is usually used, 10 times smaller - decibels (denoted by [dB]).
Energy spectra of sound signals: Russian and English, are shown in Figure 4.7. The spectra of these signals have differences, but the maximum components of these spectra (as well as the speech spectra of other languages) lie in the frequency range of 0.6 ... 1.0 kHz. In general, speech is a broadband process, the frequency spectrum of which extends from 50 ... 100 Hz to 8 ... 10 kHz. As a result of speech studies, it has been established that quite satisfactory speech quality is maintained when the spectrum is limited to frequencies from 300 Hz to 3400 Hz. These frequencies are accepted by international and national standards organizations in the field of communications as the boundaries of the effective spectrum of speech signals.
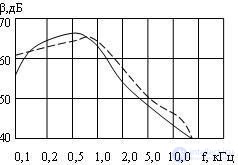
Fig. 4.7 Energy spectrum of a speech signal: ____ Russian speech, _ _ _ English speech
Communication systems focused on the transmission of speech signals should provide the necessary quality of their transmission, determined by the volume level, intelligibility, natural sound of the voice, low noise level. Radio communication systems and telephone networks designed to transmit audio messages should also take into account the following characteristics of voice signals.
The average power of the speech signal supplied to the input of the communication system must be determined by the technical characteristics of this system. In addition to the average power in the transmission of speech, there is also a distinction between power in the activity interval (signal power in the talk phase) and threshold power (signal power in the interval of pauses).
The activity rate of a telephone message is determined by the ratio of the total time during which the signal power of one of the subscribers exceeds the threshold value, to the total talk time. It is believed that each of the interlocutors in a conversation takes about 50% of the time, and also takes into account that individual words and phrases are separated by pauses. As a result, the speech signal activity coefficient is assumed to be 0.25 ... 0.35.
The dynamic range of the speech signal - the ratio of the maximum value of the instantaneous power of the signal P MAX to the minimum value of the instantaneous power P MIN , or in logarithmic units
D - = 10 lg (Р MAX / Р MIN ), [dB]. (4.14)
In expression (4.14), the value of signal power that can be exceeded only during 2% of the total transmission time is taken as P MAX ; and for the value of P MIN they take such a signal power value, which must be exceeded for 98% of the total time.
In sound broadcasting programs, signals carry information contained in not only the sounds of speech, but also musical instruments and other sources of sound. An increase in the amount of information transferred is accompanied by a change in the characteristics of communication systems. The quality of the transmitted audio broadcasting signals is determined by the class of the broadcast channel. For example, the frequency range carried by the signals of the first class broadcasting is limited to frequencies of 0.05 ... 10.0 kHz (high enough quality). The best characteristics of signal transmission are provided by the highest quality channel (0.03 ... 15.0 kHz).
Dynamic range of audio broadcasting program signals: the speaker's speech is 25 ... 35 dB; art reading - 40 ... 50 dB; vocal and musical instruments - 45 ... 55 dB, symphony orchestra - up to 65 dB
In television broadcast programs, audio messages are added to optical messages, as well as additional information necessary for the coordinated operation of the transmitting and receiving devices. Television broadcast signals will be discussed in more detail in subsequent sections. Here we note only the main characteristics of the signals broadcast television.
The standards of television broadcasting in different countries may be different. In our country, the frequency range from 0 to 6 MHz is used to transmit black and white signals. Chroma signals are transmitted in the same frequency range as black-and-white signals. Color television must be compatible with black and white, that is, black and white programs must be equally perceived on color and black and white receivers. At the same time, color transmissions on black and white receivers should be perceived as black and white transmissions.
Audio signals occupy a separate frequency band in the spectrum of a television signal. The dynamic range of the television signal is approximately 40 dB.
Comments
To leave a comment
Devices for the reception and processing of radio signals, Transmission, reception and processing of signals
Terms: Devices for the reception and processing of radio signals, Transmission, reception and processing of signals