Lecture
radio signal fusers perform 2 main functions:
1) amplification of modulated cokes *** (radio signals) to the frequency converter, i.e. at the frequency of the carrying col *** and after the converter, i.e. at intermediate frequency;
2) providing frequency selectivity, for which these amplifiers contain resonant circuits: triple circuits, filters, etc.
Depending on what frequency the amplification occurs, there are:
- RF amplifier (the frequency of the amplified signal varies);
- UPCH (the tuning frequency is constant).
The main electrical characteristics of radio amplifiers include the following:
1) Resonant voltage gain
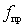 .
.
2) Resonance Gain
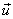 ,
,
Where 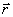 - active component of the load conductivity;
- active component of the load conductivity;
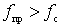 - active component of input conductance.
- active component of input conductance.
3) Selectivity, showing a relative decrease in gain at a given detuning.
4) The noise figure, which determines the noise properties of the amplifier.
5) The noise figure, which determines the noise properties of the amplifier.
6) Distortion signal in the amplifier. In the amplifier of radio signals, distortions can be: non-linear, caused by non-linear characteristics of the active element, and linear - amplitude-frequency and phase-frequency.
7) Stability of the amplifier - determined by its ability to maintain the main characteristics during operation, as well as the lack of a tendency to self-excitation.
Comments
To leave a comment
Devices for the reception and processing of radio signals, Transmission, reception and processing of signals
Terms: Devices for the reception and processing of radio signals, Transmission, reception and processing of signals