Lecture
Using fractions, the same part of the whole object can be written in different ways.
The figure shaded half a circle (1/2).
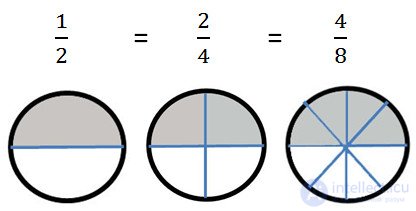
If the same circle is divided into 4 parts, then the same half of the circle can be represented as 2/4.
If the same circle is divided into 8 parts, then the same half of the circle can be represented as 4/8.
Thus, all these fractions are equal.
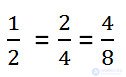
We received fraction 2/4 from fraction 1/2, multiplying its numerator and denominator by 2.
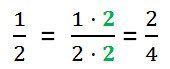
And to get 4/8, we have multiplied the numerator and denominator 1/2 by 4.
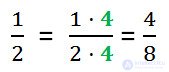
For convenience, an additional factor is recorded on the sloping line on the right above the fraction.
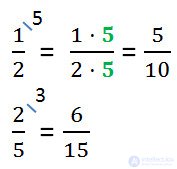
Let us return once more to our fractions and write them in a different order.
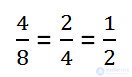
A fraction equal to this can be obtained if the numerator and denominator of the fraction are simultaneously divided into the same number that is not equal to zero.
Such a fraction conversion is called fraction reduction .
Fraction reduction is usually written as follows.
The numerator and denominator are crossed out with lines, and next to them the results of dividing (particular) the numerator and denominator by the same number are written.
The number that divided the numerator and denominator, keep in mind.
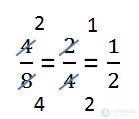
In our example, we reduced (that is, we divided both the numerator and the denominator) a fraction for a two, which we kept in mind.
Fraction reduction can be carried out sequentially.
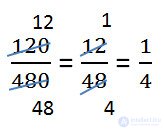
We formulate the main property of a fraction.
If the numerator and denominator of a fraction are multiplied or divided by the same number that is not equal to zero, then you will get a fraction equal to this one.
We write this property in the form of letter expressions.
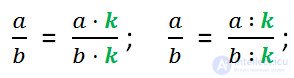 where a, b and k are natural numbers.
where a, b and k are natural numbers.
Comments
To leave a comment
Arithmetic
Terms: Arithmetic