Lecture
Let's draw a straight line. Mark the point 0 (zero) on it and take this point as the origin.
Arrow indicate the direction of movement in a straight line to the right of the origin. In this direction, from point 0, we will put off positive numbers.
That is, positive numbers are already known to us, except for zero. Sometimes positive numbers are written with a “+” sign. For example, "+8".
For brevity, the “+” sign in front of a positive number is usually omitted and instead of “+8” they simply write 8.
Therefore, “+3” and “3” are the same number, only indicated in different ways.
Choose a segment, the length of which will be taken as a unit and put it several times to the right of point 0. At the end of the first segment the number 1 is written, at the end of the second - number 2, etc.
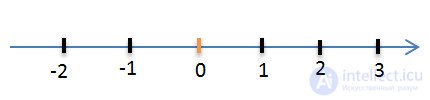
Putting a single segment to the left of the reference point, we get negative numbers: -1; -2; etc.
Negative numbers are used to denote different values, such as: temperature (below zero), flow rate — that is, negative income, depth — negative height, and others.
As can be seen from the figure, negative numbers are numbers already known to us, only with a minus sign: -8; -5.25, etc.
The number 0 is neither positive nor negative.
The number axis is usually placed horizontally or vertically.
If the coordinate line is located vertically, then the upward direction from the beginning of the reference is usually considered positive, and downward from the beginning of the reference - negative.
Arrow indicate a positive direction.
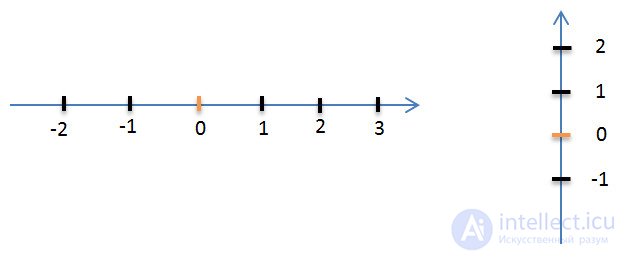
The line on which it is noted:
Comments
To leave a comment
Arithmetic
Terms: Arithmetic