Lecture
Rational numbers are integers and fractional numbers (ordinary fractions, finite decimal fractions and infinite periodic fractions).
There is a version that the name of rational numbers is associated with the Latin word "ratio" - mind.
Infinite non-periodic fractions are NOT in the set of rational numbers.
Therefore, the number "Pi" (π = 3.14 ...), the base of the natural logarithm
e (e = 2,718 ..) or √2 are NOT rational numbers.
Examples of rational numbers:
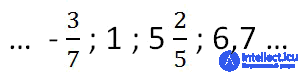
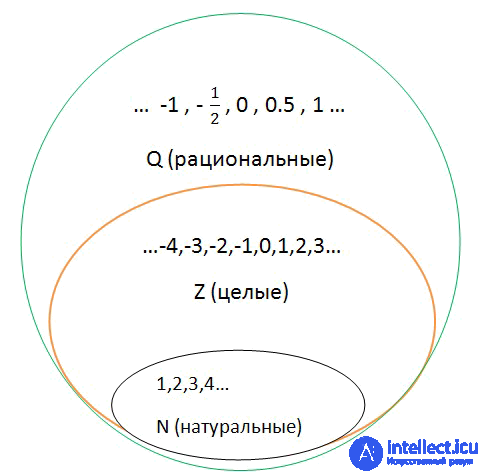
The set of rational numbers is denoted by the capital English letter Q (Q).
The set Q includes the set of integers (Z) and natural numbers (N).
Any rational number can be represented as a fraction, in which the numerator belongs to integers, and the denominator - natural.
a / b , where a ∈ Z (a belongs to integers), b∈N (b belongs to natural numbers).
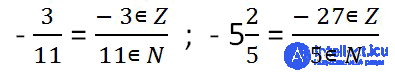
Comments
To leave a comment
Arithmetic
Terms: Arithmetic