Lecture
Special connection of juvenile group crime with alcoholism. This connection is multichannel, direct and inverse. Alcoholic excesses of minors are the ways of “adult” self-assertion, leisure activities, free communication. They are group in character. It is hardly possible to find cases when teenagers used alcohol alone. They definitely need the audience, the audience, the actions in front of it and constitute the essence of group alcoholic excesses. It is often mistakenly believed that there is only one mechanism for linking juvenile delinquency with alcoholism, namely, the commission of crimes while intoxicated, according to the formula given in fig. 2.1.
With a focus on the action of this mechanism, it is mainly trying to build preventive work. However, according to research and practice, only 25-35% of crimes are committed by persons who are intoxicated. It is this formula that is reflected in criminal statistics. At the same time, over 35% of acquisitive crimes are committed by juveniles in a sober state, but to extract funds for the purchase of alcohol. Here there is another mechanism, which is not reflected in the head statistics and is not sufficiently taken into account in preventive work, the mechanism of linking group crimes and alcoholization of minors:
It is important for employees of the OTPS, practical psychologists, social and pedagogical workers to know other social and psychological mechanisms of connection between alcoholism and group crimes of students. For example, the need for “adult” self-affirmation encourages participation in group alcoholic excesses that may result in crimes. The formula here is:
According to this formula, many of the so-called "wedding crimes" are committed, crimes during the youth's farewell service to the Armed Forces, as well as in the evening and at night while "catching the buzz" in expensive restaurants, when the group "relaxes" after a successful "case" . Acts of stabbing, the use of firearms have become commonplace with such a night "rest", especially if the group was disturbed by someone in "her" restaurant. According to formula III, more than 40% of all violent crimes, acts of vandalism and hooliganism are committed, especially at night. This indicates the importance of specific preventive work of teachers, drug treatment specialists, practical psychologists, and law enforcement officers in the field, taking into account the current situation: to know the places that attract young people, to be able to control them, to take timely measures to prevent “fights” and to clarify the relations between the groups.
So far, crime prevention has not paid enough attention to the fourth mechanism of linking juvenile group crimes with alcoholism, when systematic early alcohol consumption leads to an intense (shock) development of an alcoholic disease, accompanied by the degradation of the adolescent's personality, and the degraded personality is looking for similar ones - degrading adolescent groups - for the systematic commission of acquisitive crimes:

Fig. 2.1

Fig. 2.2

Fig. 2.3
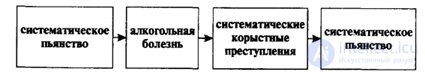
Fig. 2.4
A study of the histories of diseases of persons who were treated at medical-labor dispensaries showed that those who began to drink alcohol to minors develop an alcoholic disease 2.5–3 times faster than those who began to drink alcohol by adults. That is why anti-alcohol education of minors is important in the fight against group crime. Juveniles demoralized by systematic use of alcohol systematically commit petty theft, work as a cargo
_________________
1 See. Socio-psychological and socio-pedagogical problems of the prevention of juvenile delinquency. Sat scientific papers. M., Academy of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the USSR, 1981, p. 40-58.
________________
Chikov in stalls, commercial tents, supermarkets, begging, grouping ("heaping") in asocial and criminal groups.
In organizing the prevention of group crimes, it is important to know the typology of minors by their attitude to alcohol and the motivation of its consumption. From these positions there are the following groups of minors:
1) beginners to drink "out of curiosity";
2) use alcohol for self-assertion;
3) "lovers of buzz";
4) "alcoholic aesthetes";
5) defiant;
6) suffering from alcoholic illness.
Consider the specifics of preventive work with each of these groups of alcoholizing adolescents.
The development of alcoholism begins with the seemingly harmless, at first glance, use of alcohol - out of curiosity. Having satisfied their natural curiosity at this age, some of the minors never drink alcohol again.
For others who have experienced a state of alcohol intoxication, drinking alcohol in peer groups or with the participation of adults acquires personal meaning when drinking becomes a means of self-affirmation. Such alcoholic excesses usually have a group character, must have a so-called audience, in whose eyes you must assert yourself (your group, other peers or adults). The group of alcoholizing adolescents easily turns into a "skop", choosing to self-affirmation as a means of drunken courage, hooliganism, demonstration of force, acts of vandalism, fighting, stabbing, etc.
Otherwise, the group criminal behavior of minors develops when alcohol is used in traditional rituals as a component of leisure. These include groups of "lovers of high", as well as "alcoholic aesthetes", in which social dependence on alcohol is complemented by psychological dependence. The first drink to experience alcoholic euphoria, and the second reinforce the use of alcohol with their own "theories": what and how you should drink to get pleasure and enjoyment. The initiators who set the tone are minors, or adults, whose drinking has become one of the ways to fill free time, have fun, and associate with certain perversely understood aesthetic values. Out of solidarity or under psychological pressure, other adolescents are joining them, for whom in a state of intoxication it is easier to demonstrate their superiority over others, to feel self-confidence, to show themselves as "men."
"Alcoholic aesthetes" tend to involve girls in drinking, soldering, organizing dens, and committing acts of rape. In groups of "lovers of buzz" and "alcoholic aesthetes" criminal behavior becomes an addition to alcoholic excesses, since it is impossible to completely fill leisure time with just the use of alcohol.
The groups of adolescents flaunting the use of alcohol have the greatest criminal risk. The essence of this bravado - in the desire to "drink everyone". Their leisure is primitive. Such a meaningful desire for alcohol (“I will drink half a liter and not get drunk”, “my norm is half a liter”, etc.) contributes to the rapid development of social and psychological dependencies into physical dependence on alcohol, leads to degradation of the personality, to that stage of alcoholic illness, when a student begins to drink indiscriminately, with whom, and with whom, and in such a state he easily goes to any crime to get money for alcohol.
Recently, a new, directly opposite attitude towards alcohol has emerged among criminal youth - a peculiar prohibition. It appeared under the influence of certain mafia structures recruiting bodyguards from among the most physically developed adolescents and young men, assistants to crack down on the recalcitrant, tribute collectors (racketeers), etc. One of the conditions for taking such groups or persons under the care of minors is a strict ban on their use of alcohol. Those who violate this prohibition are ruthlessly banished, excommunicated from the group. So some mobsters have become a kind of advocates of a sober lifestyle. Here there is also the practical interest of the mafia in the sobriety of young people. Sober ones are needed not only as bodyguards, but also as direct perpetrators of criminal plans. You can expect less failure from them, they act more efficiently.
____________
Mashkina K. None: "Doctor, how is he?" - "It will drink ..." // Moskovsky Komsomolets, 1995, October 3.
____________
Substance abuse and juvenile gang crime.
Different types of substance abuse are common among groups of juvenile offenders in order to stupefy themselves - conscious self-poisoning, and hence self-destruction. Usually adolescents inhale potent alcohol-containing substances - paints, various air fresheners in aerosol packages; use perfumery products; swallow large quantities of drugs that cause conditions that are close to narcotic; inject different mixtures of toxic substances into the veins, use household chemicals; production emulsions and dyes, various extracts of plant substances.
The motives for the use of toxic substances almost coincide with the motives for the use of alcohol. The main ones are: 1) consumption out of curiosity; 2) bravado with its courage; 3) the desire to assert themselves among themselves; 4) group involvement ("for the company"); 5) the desire to get "high" (relax); 6) the desire to have fun; 7) the desire to get away from difficult life problems; 8) remove the psychological barrier before committing other forms of antisocial and criminal behavior (before engaging in group sex, committing a crime, etc.).
Like alcoholics, all addicts tend to unite in groups for the acquisition, storage and use of toxic substances. "For the company" is easier to overcome the natural fear of toxic poisoning, it is more interesting to jointly experience the state of toxic "high". In this state, minors are characterized by increased suggestibility, conformal, group-dependent behavior. Therefore, drug addicts are in the hands of more experienced leaders ("leaders") tool of committing various types of crimes. For alcohol, its substitutes, toxic substances and drugs, addicts are ready to commit any crime. Toxic substances are often fatal1. Groups of addicts can be attributed to the primitive criminal groups of minors.
The diagnosis of addicts involves the identification of both individuals and groups that use toxic substances.
_____________
1 According to some data, up to 11 thousand adolescents die from the use of toxic substances annually. See also: Urgently in the room. Two child addicts died during a group dose / // Moskovsky Komsomolets. 1995, December 20; Bitter Accident // Moscow News. 1995, December 21st.
____________
va. To detect drug addicts can be emanating from their clothes indestructible odors; carrying with them various containers (bubbles) with liquids, plastic bags in which the liquid is sprayed; wearing cotton wool moistened with a toxic liquid; shaved nape; lining on hand; the desire for grouping and solitude in the intervals between occupations in toilets and other places, etc.
In the case of detection of drug addicts, it is necessary to establish their circle of contacts, mutual relations and mutual influences; leadership in the group, as well as those who supply toxic substances to the school and college and incline students to their use.
By law, all drug addicts should be put on dispensary accounting and accounting in CPF, their treatment should be organized. In severe cases, they are immediately isolated and sent to appropriate medical institutions for inpatient treatment.
Prevention also includes: anti-toxic education; the involvement of adolescents in socially beneficial activities and in adolescent associations; individual patronage; hard total control.
Applicator - uses TV (toxic substance), imposing a moistened swab with TV on the back of the head (most often acetone).
A teenage nurse who “bald” with the help of inhalation of various volatile substances (adhesives, varnishes, solvents, etc.).
Nyuhach cellophanschik - uses volatile TV, putting on a plastic bag on his head.
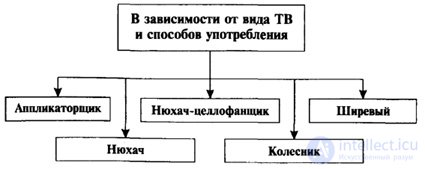
Scheme 2.1
Kolesnik ("wheel" in the jargon - a tablet) - swallows psychotropic medicinal substances, both "inhibiting" mental activity (tranquilizers), and activating it (ether-containing drugs) 1.
Shirevy is a teenager who has “sat down on a needle,” who injects non-drug-related toxic substances into his vein (for example, tobacco infusion).
Thus, the complex and multilateral relationship of juvenile group crime and alcoholism, the difference between adolescents in relation to the use of alcohol and other intoxicating drugs must be taken into account and in accordance with this differentiate the prevention of group crimes. Due to the disgraceful failure of the anti-alcohol campaign, as one of the main means of uniting minors into asocial and criminal groups, it is difficult to oppose alcoholic excesses, to find such a complex of socially useful free-time activities that can enthrall minors, unite and rally them into positively directed groups . And yet we must look, not relying on miraculous measures in the fight against group crime of adolescents and youths.
Drug abuse and juvenile gang crime.
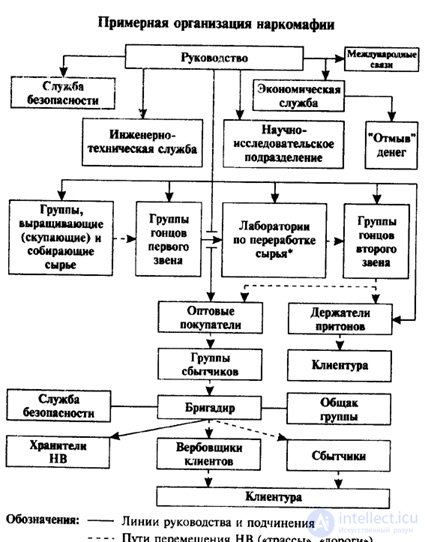
Special attention should be paid to police officers and pedagogical workers to work on the prevention of group crime associated with drug addiction2. According to the Interior Ministry, there are 2.0 million drug addicts in Russia. By 2000, their number will double. More than 20 million people, mostly young people, have tried drugs3. Drug addiction is an extremely complex socially negative phenomenon, consisting in the manufacture, storage and sale of narcotic substances. This is the most profitable sphere of criminal business, acquiring an ever more international character, in which an important place is given to minors and young people, both drug users and subjects of criminal fishing. Alone here do not work. Usually a group of drug addicts is headed by an adult or a young man who has served a sentence in a correctional institution or returned from a special school. A group of addicts are peculiar to:
________________
1 See. Morozov E. Deadly high // World news. 1996, February 12th.
2 In 1994, of the total number of drug-related criminal acts disclosed, 10% were women and 5% were students. See: Pitirimova O. Way-ways of the "dope" // Shield and sword. 1995, No. 42.
3 A. Kondrashov. Red light of "white death" // Arguments and Facts. 1995, No. 35.
___________
pronounced conspiracy, corporatism, a clear distribution of roles in the group, strict subordination, its own laws and rules of conduct, identification signals. Often, a group engaged in the manufacture, storage and sale of drugs is identified with drug addicts, i.e. drug users, which is illegal. The group that chooses to distribute drugs as a means of enrichment, as a rule, does not use drugs. She only makes, stores, sells drugs, involves other people in drug addiction, organizing dens and inclining to the use of narcotic substances. But drug addiction necessarily generates a number of adjacent and related group crimes. We list the main ones:
1) illicit sowing or cultivation of opium poppy, Indian, southern, Manchurian cannabis and other crops prohibited for cultivation, containing narcotic substances;
2) their transportation from the growing regions to other areas of the country through the secret channels of groups of drug addicts;
3) forgery of prescriptions for the purchase of drugs of narcotic action;
4) sale of prescriptions or drugs themselves intended for medicinal purposes;
5) the organization or maintenance of dens for taking drugs or the provision of premises for the same purposes;
6) commission in a state of drug intoxication of group crimes or the commission of crimes to obtain funds for the purchase of drugs (theft, robbery, robbery, etc.);
7) the creation of clandestine laboratories for the manufacture of synthetic drugs, screw-type narcotics (non-addictive) 1 and the use of secretions of living organisms (certain types of arachnids) to achieve drug intoxication.
Comments
To leave a comment
Criminal psychology
Terms: Criminal psychology