Lecture

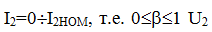 changes, that is, below by a few%.
changes, that is, below by a few%.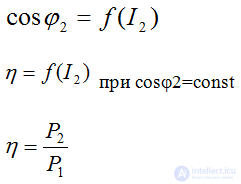
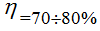 low-power transformers
low-power transformers
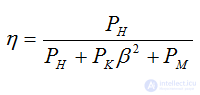
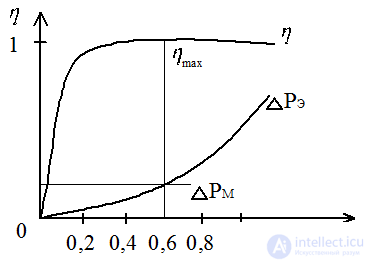
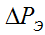 - electrical losses
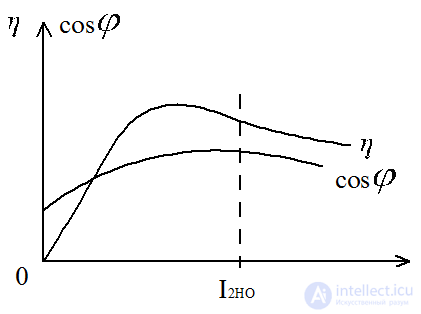
- electrical losses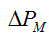 - magnetic losses depend on the load factor
- magnetic losses depend on the load factor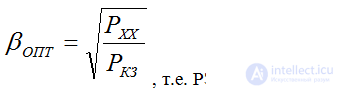
The external characteristic of the transformer is the dependence of the voltage of the secondary winding U 2 on the current I 2 . If we ignore the no-load current, then the equivalent circuit of a transformer in nominal mode takes the form shown in Figure 1.
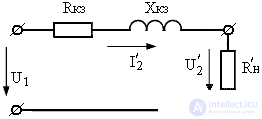
Considering that Z kz = R kz + jX kz , the voltage on the secondary winding of the transformer can be expressed as follows:
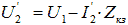 (one)
(one)
Construct a vector diagram relative to the current vector 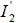 as shown in Figure 2.
as shown in Figure 2.
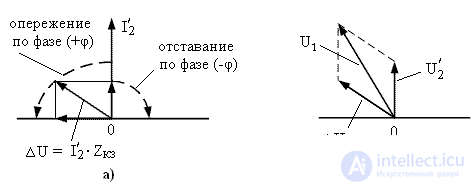
If the load resistance 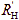 active then the voltage
active then the voltage 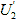 coincides in phase with the current
coincides in phase with the current 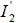 . Amount
. Amount 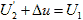 . The magnitude of the applied voltage U 1 = const , it is obvious that when the current changes
. The magnitude of the applied voltage U 1 = const , it is obvious that when the current changes 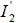 , the voltage drop Δ U on the internal resistance of the transformer will also change. That is, the external characteristic has a falling character, as shown in Fig. 2.25.
, the voltage drop Δ U on the internal resistance of the transformer will also change. That is, the external characteristic has a falling character, as shown in Fig. 2.25.
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design