Lecture
Task 3
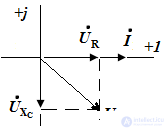
Build a qualitative vector diagram.
The construction is carried out using the properties of the elements. The current vector is first constructed, then the voltage vector. 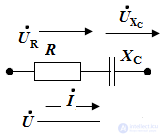
Task 4
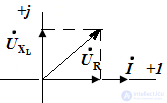
Build a qualitative vector diagram.
The construction is carried out using the properties of the elements. 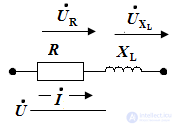
Task 5
Construct a qualitative vector diagram for the circuit, provided that XL> XC.
The construction is carried out using the properties of the elements. 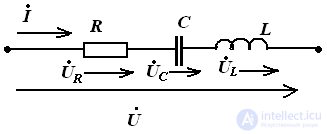
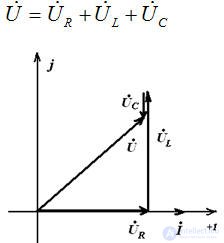
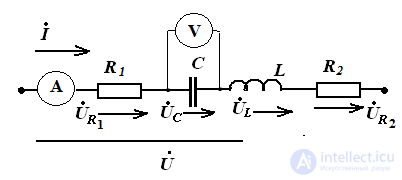
Task
In the series circuit, determine the readings of the instruments, compile and calculate the power balance, determine the power factor, build a topographic vector diagram.
R1 = 10 ohm
R2 = 20 ohm
C = 31.8 microfarad
L = 0.127 GN
f = 50 Hz 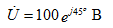
Decision:
one). Determine the total complex resistance of reactive elements 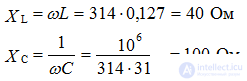
2). We translate the source voltage into algebraic form 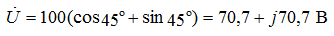
3). Determine the equivalent circuit resistance 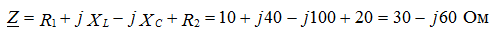
The circuit has an active-capacitive character.
four). Determine the current in the circuit 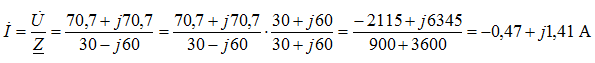
five). Ammeter will show the current value of current 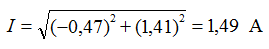
6). Determine the reading of the voltmeter, the effective value of the voltage on the capacitor 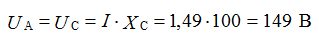
7). Determine the power source and receivers 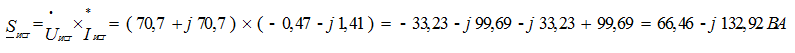
Receiver power 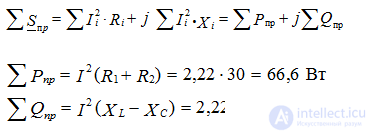
From the calculations it is clear that the balance converges with an error of less than a percent. 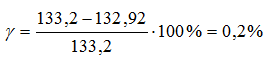
eight). Determine the power factor 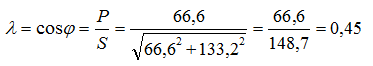
9) construction of a topographic vector diagram
Determine the voltage on the circuit elements 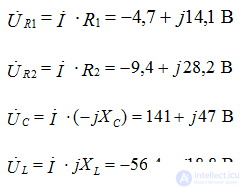
The choice of the scale of the current 2 cm - 1 A; on voltage 2cm - 50 V
The rule of construction of the vector diagram, with the sequential inclusion of elements:
build a current vector
build stress vector
we add the stress vector according to the parallelogram rule. 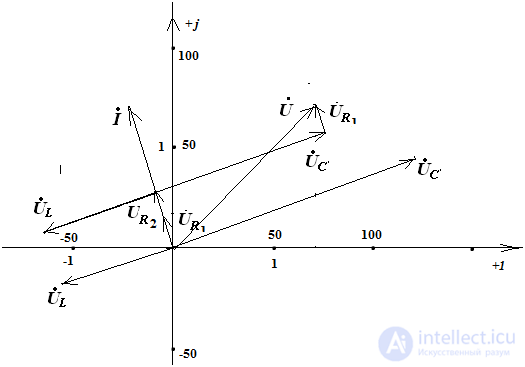
parallel connection example
Determine the currents in the branches.
Given: 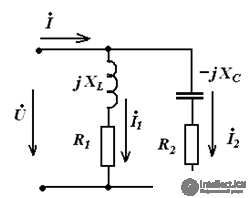
R1 = 10 ohm
R2 = 10 ohm
f = 50 Hz 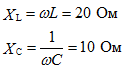
Decision:
3 branches, 2 knots.
Currents are determined by Ohm’s law. We write the full resistance of the branches: 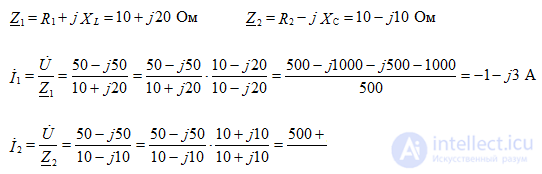
The total current is determined by the first Kirchhoff law 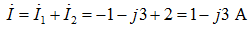
Vector diagram 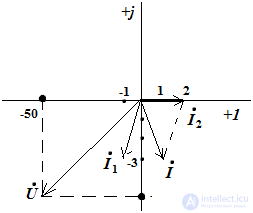
Task 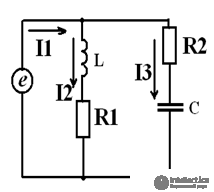
E = Uo + Um • sin (ωt + 45), Uo = 45 B, U = 39 B,
R1 = R2 = 50 Ohm, L = 0.127 GN, C = 3.18 μF
Determine Uc, I2
Decision
on a constant component
Е1 = Uo = 45 B I2 = Uo / R1 = 0.9 A I3 = 0 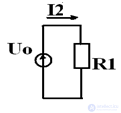
On the variable component XL = 40, Ohm Xc = 1000 Ohm 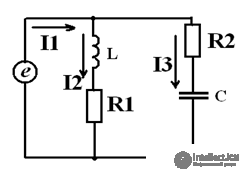
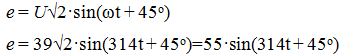
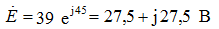
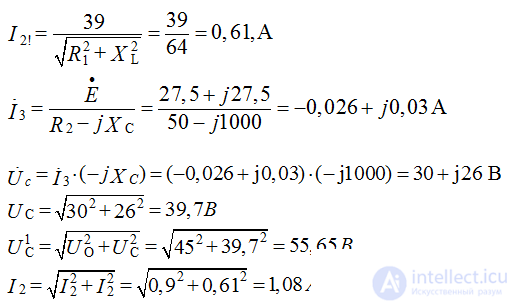
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design