Lecture
1st Maxwell's equation is the law of total current 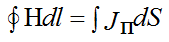
contour integral over a closed line l from H passing through a closed surface
H - magnetic field strength
H = B / μ0, in the case of vacuum,
J = σ • E - Ohm's law
Jп = J + Jcm is the total current, as the sum of the transfer current of electric charges and the displacement current, the density of which is:
where D = εε0 • E is the electric charge shift
Designations
σ - electrical conductivity (shows friction, with the passage of charges)
Q - charge in volume
ψ - electric displacement vector flux
ρ is the average charge density
P - electric polarization
M - magnetization
The simplest case of the 1st equation 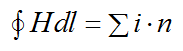
2nd Maxwell Equation - Electromagnetic Induction Law
emf induced in a closed loop by a varying magnetic field is equal to the rate of decrease of the magnetic flux coupled to the circuit in question. 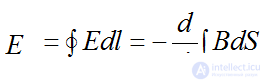
3rd equation for the electrostatic field (Gauss theorem)
The flux of the vector of electrical displacement, coming out through a closed surface, is equal to the charge contained inside this surface. The charge expresses the volume integral of its density over the volume of the surface under consideration. 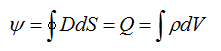
For magnetic field
The magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero.
B = μμ0 • H 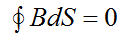
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design