Lecture
Task 1
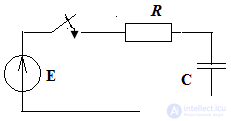
Build a transient when locking the key.
E = 10 V, C = 10 μF, R = 1 kΩ
τ = RC = 0.01s - the capacitor charging time constant
Uc lane = Uc mouth + Uc cv Uc mouth = E = 10 V
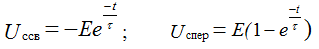
the transition process takes place exponentially.
τ is the time constant during which the free component of the process decreases in 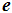 times compared with the initial condition.
times compared with the initial condition.
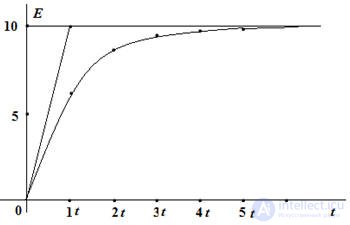
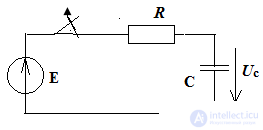
let's calculate some characteristic points:
t = τ Uc per1 = 10 (1 -1 / 2.7) = 6.3 B
t = 2τ Uc per2 = 10 (1 -1 / 7.29) = 8.63 B
t = 3 τ Uc per3 = 10 (1 -1 / 19,863) = 9.5 B
t = 4 τ Uc per4 = 10 (1 -1 / 53,14) = 9.85 B
t = 5 τ Uc per5 = 10 (1 -1 / 143,5) = 9.9 B
Task 2
Build a transition process when opening the key.
Initial conditions Uc = E = 10 V, C = 10 μF, R = 1 kΩ
τ = RC = 0.01s - the capacitor charging time constant
The time constant during which the free component of the process decreases in 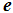 times compared with the initial condition.
times compared with the initial condition.
Uc per = Uc mouth + Uc cc Uc mouth = 0 V
Uc per = Uc cb = the transient process is exponentially.
let's calculate some characteristic points:
t = τ Uc per1 = 10 / 2.7 = 3.7 B
t = 2τ Uc per2 = 10 / 7.29 = 1.37 B
t = 3 τ Uc per3 = 10 / 19,863 = 0.5 B
t = 4 τ Uc per4 = 10 / 53,14 = 0.15 B
t = 5 τ Uc per5 = 10 / 143.5 = 0.1 B
Task 3
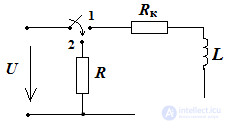
In the circuit, the inductive coil is disconnected from the DC voltage source and closed to the resistor
U = 110 V, L = 5 GN Rc = 4 Ohms, R = 6 Ohms
Find the current in the coil at t = 1 sec, it after disconnecting from the source and the voltage on R at the initial moment after switching
Solution when the source is connected to the coil (key 1 position) the current in the circuit is determined according to Ohm's law I = U / Rk = 110/4 = 27.5 A
After switching, i.e. key switching (key position 2) the electrical state of the circuit is described by the equation
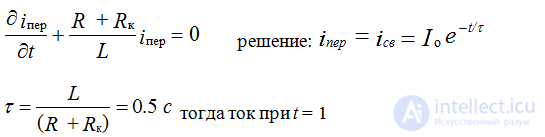
Voltage UR = RI = 27.5 ∙ 6 = 165 B
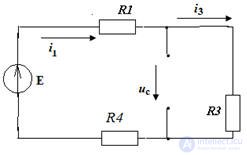
Task 4
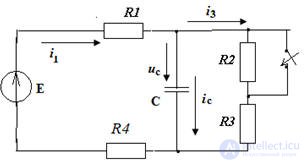
Given: E = 100 V; R1 = 20 Ohm; R2 = 30 Ohm; R3 = 10 Ohm; R4 = 40 Ohm; C = 100 μF
Determine input current 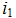 and write the expression
and write the expression 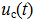
Decision
1. After closing the key
We write the equation according to the laws of Kirchhoff
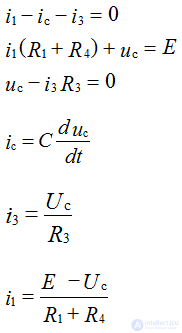
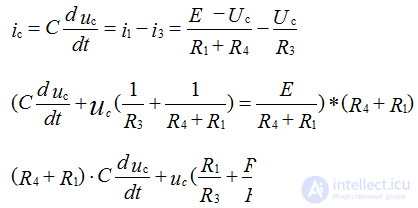
2. The calculation of the steady state
Uc = Us mouth + Uc cv
Equation for steady state:
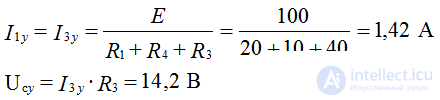
3. Solve one of the methods by determining the parameters of the transient characteristics through the solution of the characteristic equation. Let's make this equation:
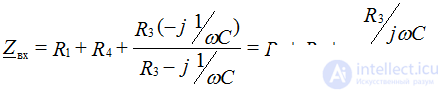
Replace jɷ = p where p is the root of the characteristic equation
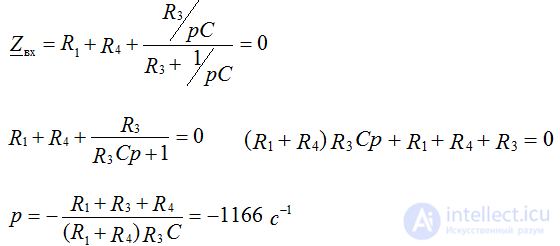
4. When t = 0: 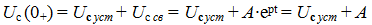
Uc (0+) = U (R2 + R3) / (R1 + R2 + R3 + R4) = 40 B
Determine the value of A: 40 = 14.2 + AA = 25.8 B
The expression of the voltage on the capacitor takes the form: 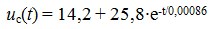
5. Write the expression for the input current. 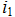
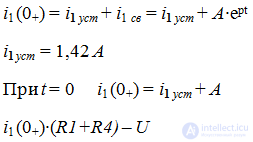
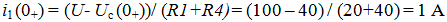
Determine the value of A: A = - 0,42
expression for input current 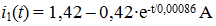
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design