Lecture
(four-wire network) 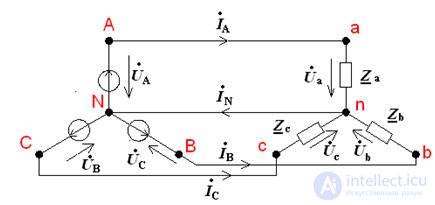
The points n and N are connected, therefore the potential of the point n is 0. 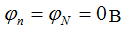
The phase voltages of the receiver are equal to the phase voltage of the generator, i.e. 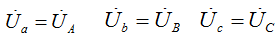
respectively, linear voltages are also equal. Thus, two voltages are applied to the receiver connected by a star: phase and linear, and the phase current is equal to the linear property of the series connection 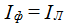 .
.
Symmetric and unbalanced load
With a symmetrical load when 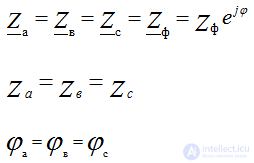
Unbalanced load 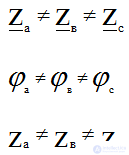
Currents at asymmetrical and symmetrical load
The mode of each phase does not depend on the mode of the other two phases - the current is determined by the parameters of the receiver of this phase, i.e. 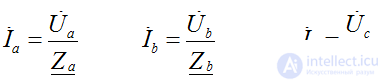
The current in the neutral wire is equal to the sum of the phase currents according to the 1st Kirchhoff's law: 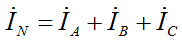
A four-wire connection is used for an asymmetrical load, since when the operation of one phase changes, the modes of the other phases will not change, because neutral wire provides constant phase voltages.
The currents in the phases have the same magnitude and are phase shifted relative to the corresponding phase voltages by the same angle φ, i.e. form a symmetric three-phase vector system on the complex plane.
Currents with symmetrical load.
According to the 1st Kirchhoff law with a symmetrical load: 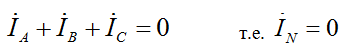
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design