Lecture
Divergence (divergence) of the force vector F 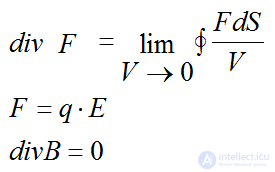
Any charge q being in an electric field of strength E is experiencing a force F.
Rotor (vortex of force vector F) lines of force 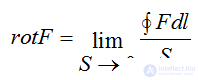
1st Maxwell's equation 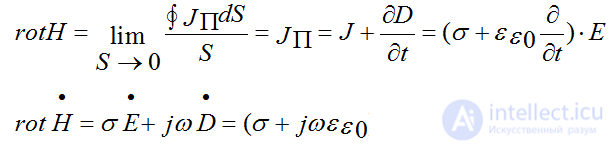
Differentiation is replaced by jω in the case of a simple harmonic signal
2nd Maxwell's equation the case of magnetic permeability 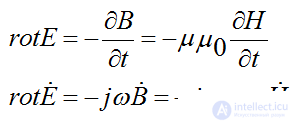
3rd equation Gauss equation for electrostatic field
The divergence of the electric displacement vector is equal to the electric charge density 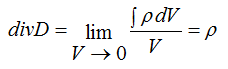
in case of constant permeability: 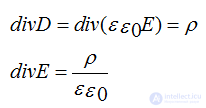
Relationship between vectors
J = σ • E - Ohm's law
D = ε0 • E + P
H = B / μ0 -M
Conductor with current divH = 0
Inside conductor rotH = J ≠ 0
There is no current in the outer region of the conductor. RotH = 0
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design