Lecture
In the lossless line absorbed by the receiver, the active power is zero.
This is possible in the following cases:
When idle
Short circuit
With purely reactive load
A standing wave is a process resulting from the superposition of forward and reverse waves with the same amplitudes.
Idling
I2 = 0 Z2 = ∞
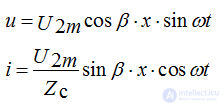
Equations of standing waves for instantaneous currents and voltages with ñ = 1
At any time at the end of the line X = 0 and at points spaced from the end of the line at distances
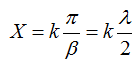
where k is an integer, when voltage peaks are obtained called antinodes, and current zeros, called nodes. Nodes and antinodes are always immobile.
The current is ahead of the voltage by 90 and vice versa.
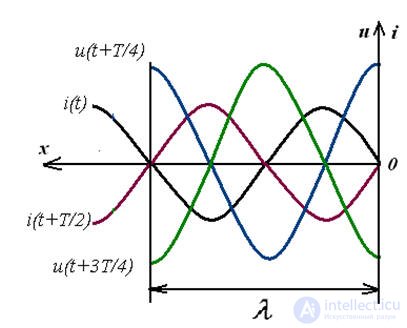
At the distance from the end of the line we have the opposite nodes of voltage and current antinodes.
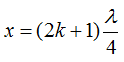
The input impedance is purely reactive and is determined by the wavelength (line) and frequency f.
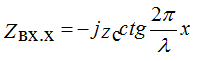
If x = 0 ÷ λ / 4 and x = λ / 2 ÷ 3λ / 4 line represents the capacitance.
If x = λ / 4 ÷ λ / 2 and x = 3λ / 4 ÷ λ, the line represents inductive resistance.
If x = 0, λ / 2, λ, etc. the line seems to be a parallel resonant circuit.
If x = λ / 4, 3λ / 4, etc. the line is represented as a sequential contour
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design