Lecture
We introduce the concept of complex resistance, which is determined by the ratio of the complex amplitude of the voltage to the complex amplitude of the current. 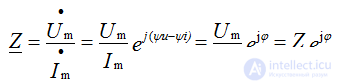
The modulus of the impedance is equal to the ratio of the amplitude of the voltage to the amplitude of the current: 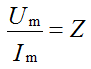
The impedance is expressed through the complex effective values of voltage and current: 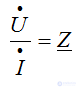
Triangle resistance 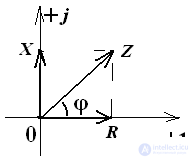
In algebraic form, Z = R + jX,
Where:
R - active resistance
X is the reactance
R = Zcosφ, R≥0,
X = Zsinφ, and the reactance can be either positive or negative or equal to zero. Thus, the vector of the total complex resistance can be only in 1 or 4 quarters of the complex plane.
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design