Lecture
Any exercises on the study of electrical engineering should begin with the study of lecture material and the corresponding section in the textbook. It is also necessary to learn the rules for compiling equations and properties of connections of elements of schemes.
Calculation of linear DC electric circuits
serial connection example 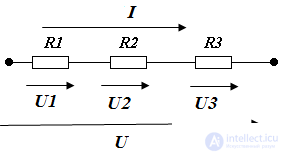
Rekv = R1 + R2 + R3
I = E / R EQ
U = U1 + U2 + U3 = R1 • I + R2 • I + R3 • I = Rekv I
Task 1
It is necessary to measure the voltage of 100 V, a voltmeter of 10 V, with an internal resistance of 10 kΩ. What to do?
Add in series to the voltmeter resistor Rdob 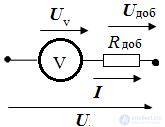
Payment 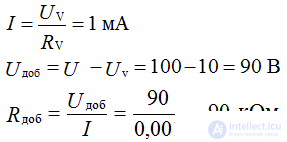
Conclusion: a serial connection, as a voltage divider, can be used to extend the range of measurement of voltmeters
Parallel - serial connection
parallel connection. 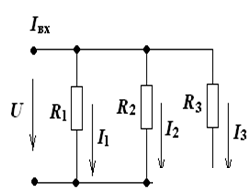
Iin = I1 + I2 + I3
I1 = U / R1 = UG1
I2 = U / R2 = UG2
I3 = U / R3 = UG3
Task
Determine equivalent resistance 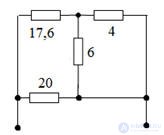
Considering this circuit, we see that the circuit has a series parallel circuit, where the resistors with resistances of 4 and 6 ohms are connected in parallel. Convert this area, we get 2.4 Ohms. Next, a 17.6 ohm resistor and a 2.4 ohm resistor are connected in series with 20 ohms, so we get 20 ohms. It remains parallel to 20 ohms and 20 ohms. The answer is equivalent to 10 ohms.
Decision 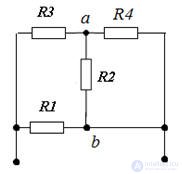
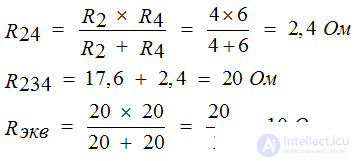
Task
Determine the equivalent resistance if R1 = R4 = R5 = 5 Ω R3 = R2 = 10 Ω 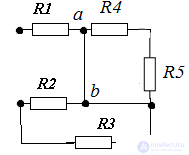
The plot with resistors R4 and R5 is shorted, therefore: 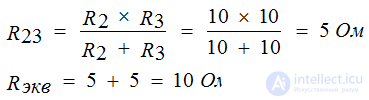
Comments
To leave a comment
Electrical Engineering, Circuit design
Terms: Electrical Engineering, Circuit design