Lecture
| Torsion is a type of deformation in which only a torque M kr occurs in a cross section of a shaft, and all other internal force factors are zero. |
| Equilibrium equation: |
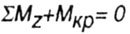 |
| Deformation - shear angle (Fig. 3.2) |
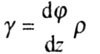 |
| Voltage |
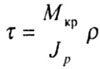 |
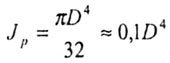 - polar moment of inertia; - polar moment of inertia; |
| D is the diameter of the rod of circular cross section, |
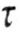 - shear stresses, p • distance from the point where it is determined - shear stresses, p • distance from the point where it is determined  to the center of the shaft. to the center of the shaft. |
| Element twist angle |
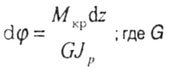 - modulus of elasticity of the second kind - modulus of elasticity of the second kind |
| Rod twist angle |
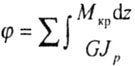 |
| The stress state is pure shear (Fig. 3.1). |
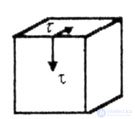 |
| Fig. 3.1 |
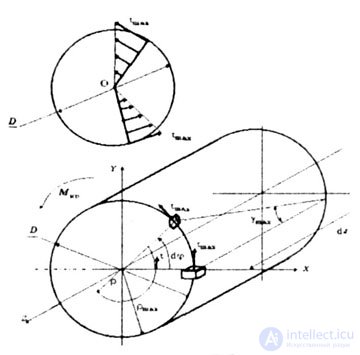 |
| Fig. 3.2 |
| Strength Condition: |
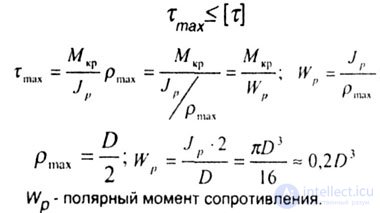 |
| For fragile materials: |
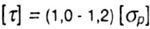 |
| For plastic materials: |
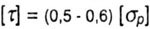 |
| Stiffness condition: |
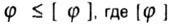 - permissible twisting angle. - permissible twisting angle. |
Comments
To leave a comment
Strength of materials
Terms: Strength of materials