Lecture
| The axial moment of resistance is the ratio of the moment of inertia about a given axis to the distance from the axis to the most distant point of the cross section |
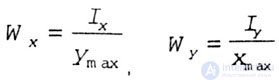 |
| The polar moment of resistance is the ratio of the polar moment of inertia to the distance from the pole to the most distant point of the cross section |
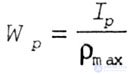 |
| The center of gravity of the cross section of the rod is taken as the pole. |
| Axial moments of resistance for the simplest sections (I xc and I yc are the central moments of inertia of the sections): |
| 1. For a rectangle (fig. 4.10). |
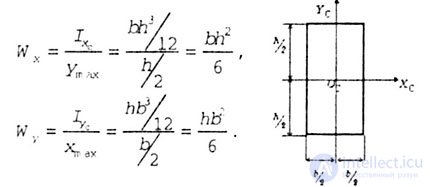 |
| 2. For a triangle (Fig. 4.11). |
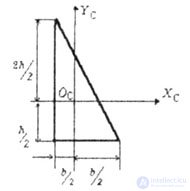 |
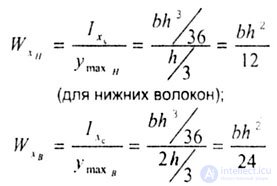 |
| (for upper fibers). |
| Similarly, you can calculate the moments of resistance about the axis of the left and right fibers W St , W pack |
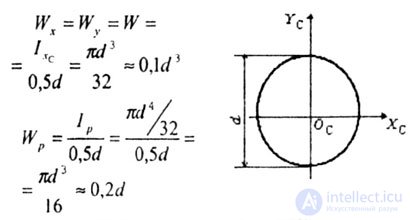
| 3. For the circle (Fig. 4.12). |
 |
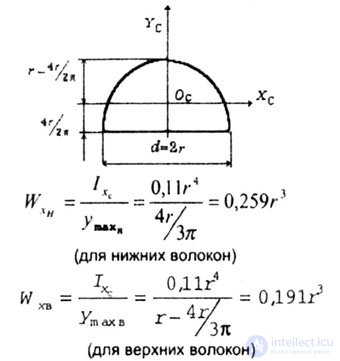
| 4. For the semicircle (Fig.4.13). |
 |
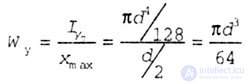 |
| 5. For tubular section (Fig. 4.14). |
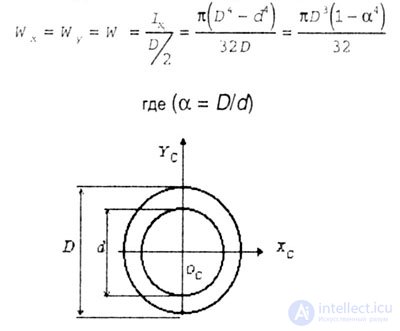 |
| Polar moment of resistance for tubular section. |
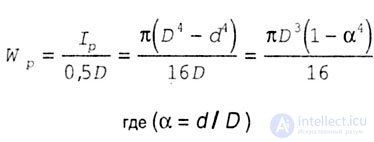 |
Comments
To leave a comment
Strength of materials
Terms: Strength of materials