Lecture
| Answers to questions about strength can give an assessment of the strength of the structure, which is reduced to a comparison of the design stresses with the allowable ones: |
 |
| These are the basic conditions of strength. |
| The design stress is the largest in magnitude compressive or tensile stress arising in a dangerous section of the structure. |
| Allowable stress. |
| Allowable stress is determined by the formula: |
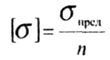 |
The mechanical characteristics of materials - the magnitude of the yield strength and tensile strength are determined empirically. Automatically plotted the graph "force - longitudinal deformation" (P -  l) This graph is translated into a stress-relative strain diagram. l) This graph is translated into a stress-relative strain diagram. 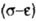 . . |
Where 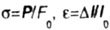 . (Here F 0 and l 0 is the initial cross-sectional area and the length of the standard sample) (Fig. 1.22). . (Here F 0 and l 0 is the initial cross-sectional area and the length of the standard sample) (Fig. 1.22). |
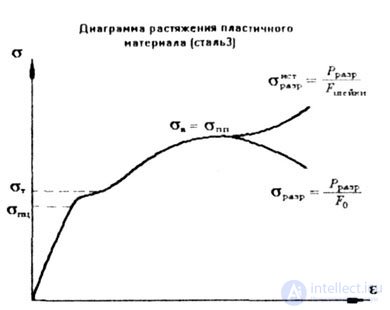 |
| Fig. 1.22 |
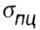 - limit of proportionality; the greatest stress at which Hooke's law is still valid; - limit of proportionality; the greatest stress at which Hooke's law is still valid; |
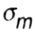 - yield point (deformations grow without an increase in load); - yield point (deformations grow without an increase in load); |
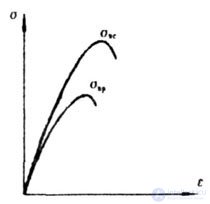 |
| Fig. 1.23 |
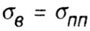 - tensile strength or temporary resistance to rupture (Fig. 1 23). - tensile strength or temporary resistance to rupture (Fig. 1 23). |
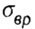 - ultimate tensile strength, - ultimate tensile strength, |
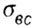 - strength of compression, and: - strength of compression, and: |
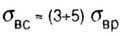 |
| When plastic material is used as the ultimate stress |
 - accepted yield strength under tension - accepted yield strength under tension 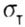 corresponding to the beginning of the material's fluidity, and in the case of a brittle material - ultimate strength corresponding to the beginning of the material's fluidity, and in the case of a brittle material - ultimate strength 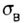 under tension or compression, preceding the sample break. under tension or compression, preceding the sample break. |
| The denominator is the normative (required) safety factor relative to the yield strength and tensile strength n, respectively. |
| It is a value greater than one, depending on the class of the structure (capital, temporary, etc.), its service life, load (static, cyclic, etc.), possible non-uniformity of the material production and the type of deformation (tension, compression, bending, etc.). |
| The standard factor of safety is regulated for building structures of SN and Pami, for machine building - by internal factory norms. In most cases, it is assumed to be equal for plastic materials: n T = 1.5 + 2.5, for fragile materials, n B = 2.5 + 5. |
| In the case when the decisive for the strength of the structure are not normal, but the tangential stresses (for example, when torsion bar round cross-section), the strength condition is: |
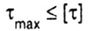 |
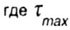 - design shear stress. - design shear stress. |
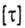 - allowable shear stress, determined by the formula: - allowable shear stress, determined by the formula: |
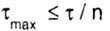 |
In the case of plastic material as the ultimate 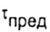 take shear yield strength take shear yield strength 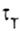 in the case of brittle material - ultimate strength in the case of brittle material - ultimate strength 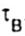 . . |
In most cases, the allowable stress in torsion is taken depending on the allowable stress in tension of the same material. For example, for steel 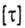 = 0.5 [ = 0.5 [ 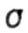 ] for cast iron ] for cast iron 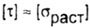 . . |
| In the practice of engineering calculations, it is considered possible to allow overvoltage of the material up to 3-5%. |
| The stiffness condition is logically constructed in the same way as the strength condition. However, restrictions are imposed not on stresses, but on changing the shape of the rod (shaft, beam), i.e. deformations. For different types of loading, the conditions of rigidity have the form: under tension (compression) |
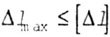 |
| torsional |
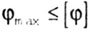 |
Where 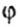 - the angle of twist, - the angle of twist, |
| bending |
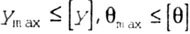 |
Where 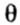 - angle of rotation, y - deflection. - angle of rotation, y - deflection. |
Comments
To leave a comment
Strength of materials
Terms: Strength of materials