Lecture

Bigraf
A double graph or bigo- graph is a mathematical term for graph theory, denoting a graph whose set of vertices can be divided into two parts in such a way that each edge of the graph connects one vertex from one part to some vertex of another part, that is, there is no edge connecting two vertices from the same part.

Full bipartite graph 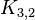
Undirected graph 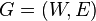 is called bichromatic if the set of its vertices can be divided into two parts
is called bichromatic if the set of its vertices can be divided into two parts 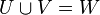 ,
, 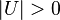 ,
, 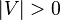 , so that
, so that
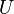 not connected to vertices in
not connected to vertices in 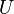 and
and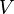 not connected to vertices in
not connected to vertices in 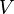
A bipartite graph is called a complete bipartite graph (this concept is different from a complete graph, that is, one in which each pair of vertices is connected by an edge) if for each pair of vertices 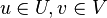 there is an edge
there is an edge 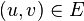 . For
. For
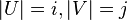
such a graph is denoted by the symbol 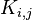 .
.
Bichrophic graphs naturally occur when modeling the relationship between two different classes of objects. For example, the count of football players and clubs, the edge connects the corresponding player and the club, if the player played in this club. More abstract examples of bipartite graphs:
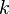 elements of one of the shares are associated with at least
elements of one of the shares are associated with at least 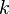 elements of another (Hall theorem).
elements of another (Hall theorem). 
Check of dichotomy with parity of distances
In order to check the graph for bipartite, it suffices to select any vertex in each connected component and mark the remaining vertices during the traversal of the graph (for example, search wide) alternately as even and odd (see illustration). If there is no conflict, all even vertices form a set 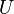 , and all odd -
, and all odd - 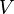 .
.
Comments
To leave a comment
Discrete Math. Set theory. Graph theory. Combinatorics.
Terms: Discrete Math. Set theory. Graph theory. Combinatorics.