Lecture
The communication process is the process of transmitting information from one person to another or between groups of people through different channels and with the help of various communication tools (verbal, extralinguistic, non-verbal).
Structural models of communication.
| SPEAKER - SPEECH - LISTENER |
|---|
| Who! | Tells what? | Which channel? | To whom? | What effect? |
| Communicator | Message | Channel | Recipient (recipient) | Effect (backlash) |
| Management analysis | Content analysis | Analysis of means and channels | Audience analysis | Results analysis |
This model is similar to the previous one. It is based on the analogy with the telephone.
This model contains the following components. The source is the one who makes the call (transmits the message). Message - transmitted information.
A telephone transmitter is an encoder that converts sound waves into electrical impulses. Telephone wire - channel. A telephone receiver (second unit) is a decoder that performs the reverse conversion of electrical impulses into sound waves, the receiver is the person to whom the message is addressed.
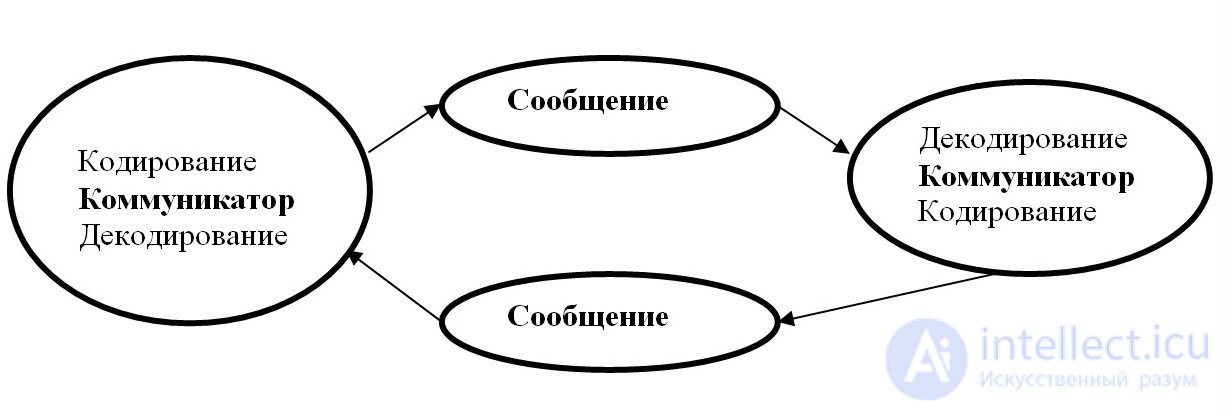
This model is proposed by the American communicativeist D. Berlo.
| SOURCE - COMMUNICATION - CHANNEL - RECIPIENT |
|---|
Berlo's model is designed to analyze in detail each of the elements of the communicative process. The source and the recipient are analyzed in terms of their communication skills and knowledge, socio-psychological attitudes, etc. The message is viewed from the perspective of its elements and structure, content and method of coding. The communication channels are the five senses, through which information flows.
Comments
To leave a comment
Communication theory
Terms: Communication theory