Lecture
Objective: to investigate and study the list data structures. The task of the work: to master the skills of writing programs for the study of list structures in the programming language PASCAL. Operating procedure :
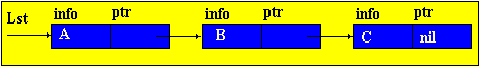
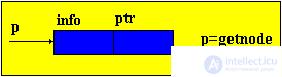
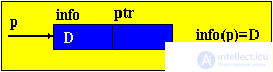
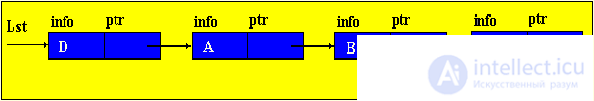
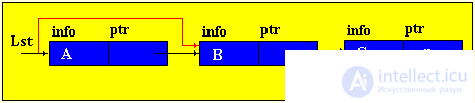
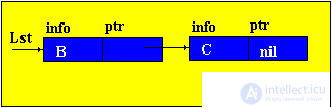
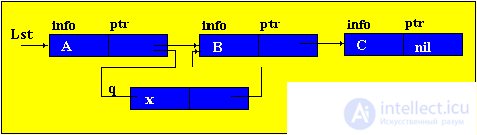
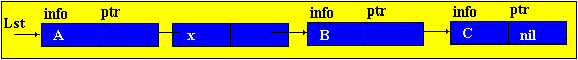
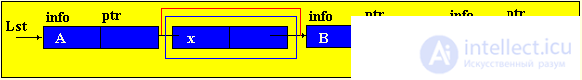
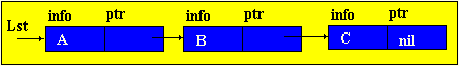
Brief theorySo far, we have considered only static program objects. This term refers to objects that are generated immediately before the execution of the program, exist during the entire time of its execution and the size of the values of which do not change during the execution of the program. Since static objects are generated before the execution of the program and the size of their values can be distinguished at the stage of translation of the source text of the program in the language of the machine. However, the use of only static objects in programming can cause certain difficulties, especially from the point of view of obtaining an efficient machine program, and such efficiency can be extremely important in solving a number of problems. The fact is that sometimes we do not know in advance not only the size of the value of a program object, but even whether this object will exist or not. Such software objects that already appear during program execution are called dynamic objects. In the PASCAL language for working with dynamic objects, a special data type is provided - the so-called reference type. The value of this type is a reference to a program object, through which the object is directly accessed. In machine language, such a link is just represented by indicating the place in the memory of the corresponding object. In this case, to describe actions on dynamic objects, each such object in the program is assigned a static variable of reference type — in terms of these reference variables, and actions on the corresponding dynamic objects are described. So, dynamic data structures have two features: 1. The number of elements in the structure is not definable in advance; 2. Elements of a dynamic structure do not have a rigid linear order. They can be scattered in memory. In order to link the elements of a dynamic structure among themselves, the structure of the element in addition to the information field includes fields of pointers (links with other elements of the structure). 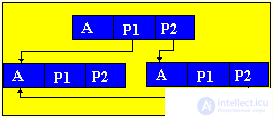 p1, p2 - pointers containing the addresses of the elements with which the element is associated. The most common dynamic structures are linked lists . From the point of view of logical representation distinguish linear and nonlinear lists. In linear lists, links are strictly ordered. The previous item pointer gives the address of the next item or vice versa. Linear lists are simply linked and doubly linked lists. To nonlinear - multiply linked lists. A list item is generally a combination of a record field (information field) and one or more pointers. Linear unidirectional lists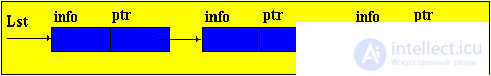 By simply-connected lists, we mean an ordered sequence of elements, each of which has 2 fields: the info info field and the ptr pointer field. The peculiarity of the pointer is that it gives only the address of the subsequent element of the list. For unidirectional lists, the index field of the last item in the list is empty nil. Lst is the index of the beginning of the list. He presents the list as a whole. Sometimes the list may be empty, i.e. There are no items in this list. In this case, lst = nil. |
Comments
To leave a comment
Structures and data processing algorithms.
Terms: Structures and data processing algorithms.