Lecture
In mathematics, it is customary to classify variables according to some important characteristics. We distinguish between real, complex and logical variables, variables representing individual values, sets of values or sets of sets. In data processing, the concept of classification plays the same, if not a big role. We will adhere to the principle that any constant, variable, expression or function is of some type.
In fact, a type characterizes a set of values that a variable or expression can take and that a function can generate.
In most programming languages, standard data types and user-defined types are distinguished. The standard includes 5 types:
a) integer (INTEGER);
b) real (REAL);
c) boolean (boolean);
d) character (CHAR);
e) index (POINTER).
To custom include 2 types:
a) enumerated;
b) range.
Any data type must be characterized by a range of values and valid operations on that data type.
This type includes some subset of integers, the size of which varies from machine to machine. If n car bits are used to represent integers in a machine, and an additional code is used, the admissible numbers must satisfy the condition -2 n-1 <= x <2 n-1 .
It is believed that all operations on data of this type are performed exactly and follow the usual rules of arithmetic. If the result goes beyond the limits of the representable set, then the calculations will be interrupted. Such an event is called an overflow.
Numbers are divided into signed and unsigned. Each of them has its own range of values:
a) (0..2 n -1) for unsigned numbers
b) (-2 N-1 . 2 N-1 -1) for sign.

When processing the machine numbers, the format is signed. If the machine word is used to record and process commands and pointers, then the unsigned format is used in this case.
Integer type operations:
a) Addition.
b) Subtraction.
c) Multiplication.
d) Integer division.
e) Finding the remainder by module.
f) Finding the extremum of a number (minimum and maximum)
g) Relational operations (comparison operations) (<,>, <=,> =, =, <>)
Examples:
A div B = C
A mod B = D
C * B + D = A
7 div 3 = 2
7 mod 3 = 1
In all operations, except for relational, the result is an integer.
Real types form a series of subsets of real numbers that are represented in computer floating point formats. Numbers
floating-point format characterized by integer values of the mantissa and order, which determine the range of change
and the number of valid signs in the representation of real type numbers.
X = +/- M * q (+/- P) is a semi-log form of the number shown in Figure 2.
937.56 = 93756 * 10 -2 = 0.93756 * 10 3
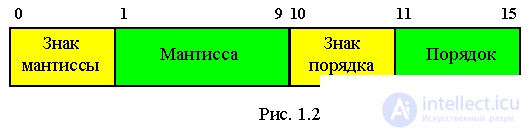
Double precision is necessary in order to increase the accuracy of the mantissa.
The Boolean standard boolean (size-1 byte) is a data type, any element of which can take only 2 values: True and False.
Logical operations are performed on logical data elements. The main ones are:
a) Negation (NOT)
b) Conjunction (AND)
c) Disjunction (OR)
Truth table of basic logical functions.
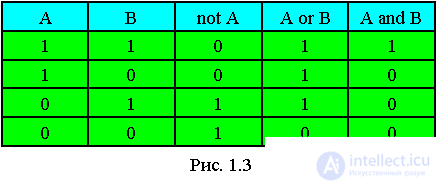
Boolean values are also obtained in relational operations with integers.
The type CHAR contains 26 uppercase Latin letters and 26 lowercase, 10 Arabic numerals and a number of other graphic characters, such as punctuation.
The subsets of letters and numbers are ordered and "adjoined", i.e.
("A" <= x) & (x <= "Z") - x is an uppercase letter
("0" <= x) & (x <= "9") - x is a digit
The type CHAR contains some unprintable character, a space, it can be
use as a separator.
Operations:
a) Assignments
b) Comparisons
c) Determining the number of this letter in the coding system. ORD (W i )
d) Finding letters by number. CHR (i)
e) Call the next letter. SUCC (W i )
f) Call the previous letter. PRED (W i )
A pointer-type variable is the physical carrier of an address of a base type value. Pointer's standard pointer type provides a pointer that is not associated with any particular base type. This type is compatible with any other pointer type.
Operations:
a) Assignments
b) Operations with unsigned integers.
Using these operations, you can calculate the address of the data. In machine form, these types occupy the maximum possible length.
For example:
ABCD: 1234 - pointer value in hexadecimal number system is a relative address.
First number (ABCD) - segment address
The second number (1234) is the address within the segment.
Getting the absolute address from the relative:
To obtain an absolute address, you need to shift the address of the segment to the left, and add the address of the internal segment to the resulting number.
For example:
ABCD0
12 3 4
----------
ACF04 is the absolute address of this number.
The enumerated type is determined by a finite set of values represented by a list of identifiers in a type declaration. Values from this set are assigned numbers according to the sequence in which the identifiers are listed. Format
type-listing declarations are:
TYPE = ();
: = , []
If the identifier is specified in the list of values of the enumerated type, it is considered the name of a constant defined in the block where the enumerated type is declared. The sequence numbers of the values in the declaration of the enumerated type are determined by their positions in the list of identifiers, with the first number in the list of constants in the list being zero. The data of the listed type includes, for example, a set of colors:
TYPE = (Red, Green, Blue)
The operations are the same as for the character type.
In any ordinal type, you can select a subset of values determined by the minimum and maximum values, which includes all values of the original type that are within these boundaries, including the boundaries themselves. Such a subset defines a range type. It is specified by specifying the minimum and maximum values separated by two points.
TYPE T = [MIN..MAX]
TYPE = [1..60]
The minimum value in determining this type should not be greater than the maximum.
Test questions:
Comments
To leave a comment
Structures and data processing algorithms.
Terms: Structures and data processing algorithms.