Lecture
Using the expression for impulse
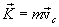
and Newton's second law can write
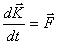 | (3.11) |
Where 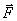 - the main vector of all external forces acting on the system.
- the main vector of all external forces acting on the system.
The last equation is a generalization of the momentum equation to an arbitrary mechanical system, since it can always be represented in the form of a system of material points interacting with each other and with external bodies. External bodies are bodies that are not part of the system under consideration, and the forces acting on the system by these bodies are external forces. Accordingly, the forces of interaction between the material points belonging to the system in question are called internal forces, and their resultant is zero. Equation (3.11) shows that the rate of change of the impulse of the mechanical system is equal to the main vector of all external forces acting on this system.
Comments
To leave a comment
Physical foundations of mechanics
Terms: Physical foundations of mechanics