Lecture
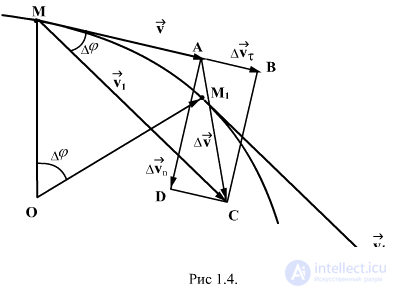
Acceleration characterizes the rate of change of speed, i.e. change in the magnitude of the rate per unit of time.
Average acceleration vector . Speed increment ratio 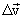 by the span of time
by the span of time 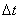 During which this increment occurred, expresses the average acceleration:
During which this increment occurred, expresses the average acceleration:
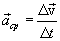
The vector, the average acceleration coincides in direction with the vector 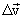 .
.
Acceleration, or instantaneous acceleration is equal to the limit of the average acceleration as the time interval tends 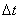 to zero:
to zero:
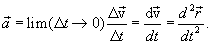 |
(1.13) |
In projections on the corresponding axis coordinates:
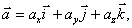
or
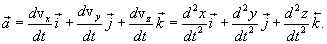 |
(1.14) |
Comments
To leave a comment
Physical foundations of mechanics
Terms: Physical foundations of mechanics