Lecture
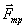 balanced by
balanced by 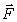 attached to the body, and
attached to the body, and 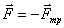 Friction, as is well known, entails heating, associated with the transformation of the mechanical motion of the rubbing bodies into the random motion of the molecules that make up the bodies. However, the impulse vector of the body
Friction, as is well known, entails heating, associated with the transformation of the mechanical motion of the rubbing bodies into the random motion of the molecules that make up the bodies. However, the impulse vector of the body 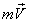 with a uniform rectilinear motion, it remains constant and in no way characterizes the amount of heat released. A single measure of various forms of motion is a physical quantity, called energy. The energy of a mechanical system quantitatively characterizes this system from the point of view of the possible quantitative and qualitative transformations of motion in it. These transformations are due to the interaction of the bodies of the system both among themselves and with external bodies. Movement is an inherent property of matter. Therefore, any body has energy, or, as is often said, a store of energy, which is a measure of its movement. For the quantitative characteristics of qualitatively different forms of motion, the corresponding types (forms) of energy are introduced, - mechanical, internal, electromagnetic, etc.
with a uniform rectilinear motion, it remains constant and in no way characterizes the amount of heat released. A single measure of various forms of motion is a physical quantity, called energy. The energy of a mechanical system quantitatively characterizes this system from the point of view of the possible quantitative and qualitative transformations of motion in it. These transformations are due to the interaction of the bodies of the system both among themselves and with external bodies. Movement is an inherent property of matter. Therefore, any body has energy, or, as is often said, a store of energy, which is a measure of its movement. For the quantitative characteristics of qualitatively different forms of motion, the corresponding types (forms) of energy are introduced, - mechanical, internal, electromagnetic, etc.
Comments
To leave a comment
Physical foundations of mechanics
Terms: Physical foundations of mechanics