Lecture
Consider the case when a material point moves from point 1 to point 2 under the action of forces applied to it (Fig.4.4.)
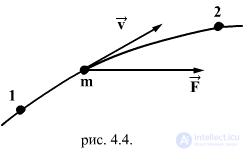
Moreover, the forces acting on a material point can have a different nature, i.e. may be conservative and non-conservative. The equation of motion in this case is written as
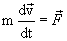 |
(4.6) |
Where 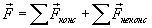
Rewrite (4.6) as
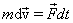 |
(4.7) |
Multiply the scalar equation (4.7) by 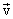 and integrate from point1 to point 2, we get:
and integrate from point1 to point 2, we get:
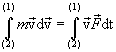 |
(4.8) |
We take into account that 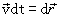 , and the integral on the right side of the expression (4.8) represents the work of all forces, in section 1-2, we can write:
, and the integral on the right side of the expression (4.8) represents the work of all forces, in section 1-2, we can write:
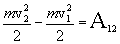 |
(4.9) |
magnitude
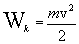 |
(4.10) |
called the kinetic energy of the material point. Thus, the kinetic energy of a material point is the energy that this point possesses due to its movement.
From the obtained expression (4.9) it follows that the work of all the forces acting on the material point on the section of the trajectory 1-2 is equal to the change of its kinetic energy on this section.
Comments
To leave a comment
Physical foundations of mechanics
Terms: Physical foundations of mechanics